Research News and Market Data on ESEA
June 18, 2025 08:00 ET
ATHENS, Greece, June 18, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Euroseas Ltd. (NASDAQ: ESEA, the “Company” or “Euroseas”), an owner and operator of container carrier vessels and provider of seaborne transportation for containerized cargoes, announced today its results for the three-month period ended March 31, 2025 and declared a common stock dividend.
First Quarter 2025 Financial Highlights:
- Total net revenues of $56.3 million. Net income of $36.9 million or $5.31 and $5.29 earnings per share basic and diluted, respectively. Adjusted net income1 for the period was $26.2 million or $3.76 per share basic and diluted.
- Adjusted EBITDA1 was $37.1 million.
- An average of 23.71 vessels were owned and operated during the first quarter of 2025 earning an average time charter equivalent rate of $27,563 per day.
- Declared a quarterly dividend of $0.65 per share for the first quarter of 2025 payable on or about July 16, 2025 to shareholders of record on July 9, 2025, as part of the Company’s common stock dividend plan.
- On March 17, 2025 the Company completed the spin-off of three of its subsidiaries containing its two older vessels, M/V Aegean Express and M/V Joanna, along with the proceeds from the earlier sale of the vessel M/V Diamantis P, into Euroholdings Ltd. (NASDAQ: EHLD). Beginning on March 18, 2025, Euroholdings Ltd. operates as an independent company.
- On May 29, 2025, the Company announced that it has signed an agreement to sell M/V Marcos V, a 6,350 teu intermediate containership built in 2005, to an unaffiliated third party, for $50 million. The vessel is scheduled to be delivered to its buyer in October 2025. The Company is expected to recognize a gain on the sale in excess of $8.50 million, or $1.20 per share.
- As of June 18, 2025 we had repurchased 463,074 of our common stock in the open market for a total of about $10.5 million, since the initiation of our share repurchase plan of up to $20 million announced in May 2022.
________________________
1 Adjusted EBITDA, Adjusted net income and Adjusted earnings per share are not recognized measurements under US GAAP (GAAP) and should not be used in isolation or as a substitute for Euroseas financial results presented in accordance with GAAP. Refer to a subsequent section of the Press Release for the definitions and reconciliation of these measurements to the most directly comparable financial measures calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP.
Aristides Pittas, Chairman and CEO of Euroseas commented:
“During the first quarter of 2025, the containership markets showed further strength, with both smaller and larger feeder segments seeing notable rate increases. This positive momentum has continued into the second quarter, with particularly strong gains in the smaller feeder segment. Market strength is also reflected in the secondhand S&P market, where demand for existing tonnage remains firm despite the continued delivery of newbuilds. Reflecting this dynamic, we successfully finalized the sale of one of our intermediate vessels, the M/V Marcos V, to an unaffiliated third party. The market strength is further reflected in our chartering activity resulting in almost 100% charter coverage for 2025 and in excess of 65% for 2026.
“Looking ahead, the containership sector may face notable challenges, primarily due to the high overall orderbook and the possibility that liner companies may resume transits through the Suez Canal. However, elevated geopolitical uncertainty driven by ongoing and escalating tensions between Iran and Israel compounded by uncertainty surrounding the U.S. Administration’s proposed tariffs add another layer of complexity. Specifically, on the supply-side while the orderbook remains high and represents the key challenge for the sector, it is heavily concentrated on larger vessel sizes. In contrast, the feeder and intermediate segments, where our fleet is concentrated, have historically low orderbooks; in addition, due to the higher proportion of older tonnage in these size segments, they are likely to experience a reduction in fleet supply over the coming years. This evolving fleet profile supports the view that, despite the potential risk of cascading from larger vessels, the fundamentals for feeder and intermediate containerships remain favorable.
“On the fleet growth front, we continue to consider ways of further modernizing our fleet. We will be soon retrofitting one more of our secondhand vessels with energy-saving devices. We have further improved our fleet profile by having transferred our two oldest ships to Euroholdings, a spin-off from our company, to pursue a separate independent market and investment strategy. Given our solid liquidity position, our Board has decided to maintain our high yielding quarterly dividend of $0.65 per share. We are also continuing our share buyback program, as our shares are trading at a substantial discount to our net asset value, despite the visibility of our revenues and earnings. As always, we remain committed to identifying attractive investment opportunities that enhance shareholder value and drive sustainable returns.”
Tasos Aslidis, Chief Financial Officer of Euroseas commented: “Our revenues for the first quarter of 2025 are increased by approximately 20% compared to the same period of 2024. This was mainly the result of the increased average number of vessels owned and operated in the first quarter of 2025, compared to the corresponding period of 2024. The Company operated an average of 23.68 vessels, versus 19.60 vessels during the same period last year. Net revenues amounted to $56.3 million for the first quarter of 2025 compared to $46.7 million for the first quarter of 2024.
“Total daily vessel operating expenses, including management fees, general and administrative expenses, but excluding drydocking costs, were $6,676 during the first quarter of 2025 compared $7,276 to the same quarter of last year. This was the result of the lower operating costs of the nine newbuilding vessels delivered during last year and in the first quarter of 2025. In the first quarter of 2024 the Company operated only five of these newbuilding vessels, while the rest were delivered gradually until January 2025.
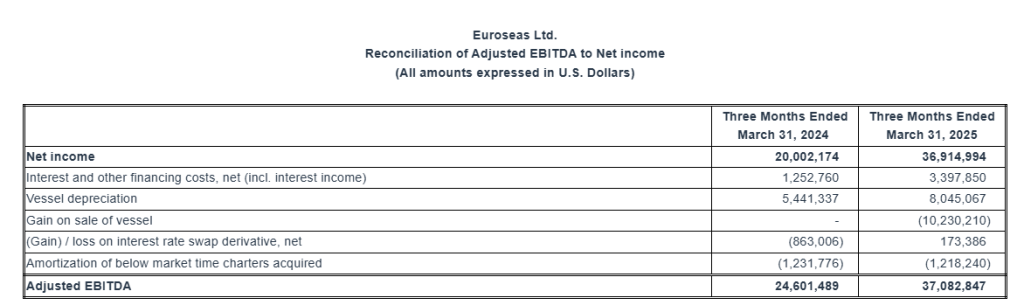
“Adjusted EBITDA1 during the first quarter of 2025 was $37.1 million compared to $24.6 million achieved in the first quarter of last year.
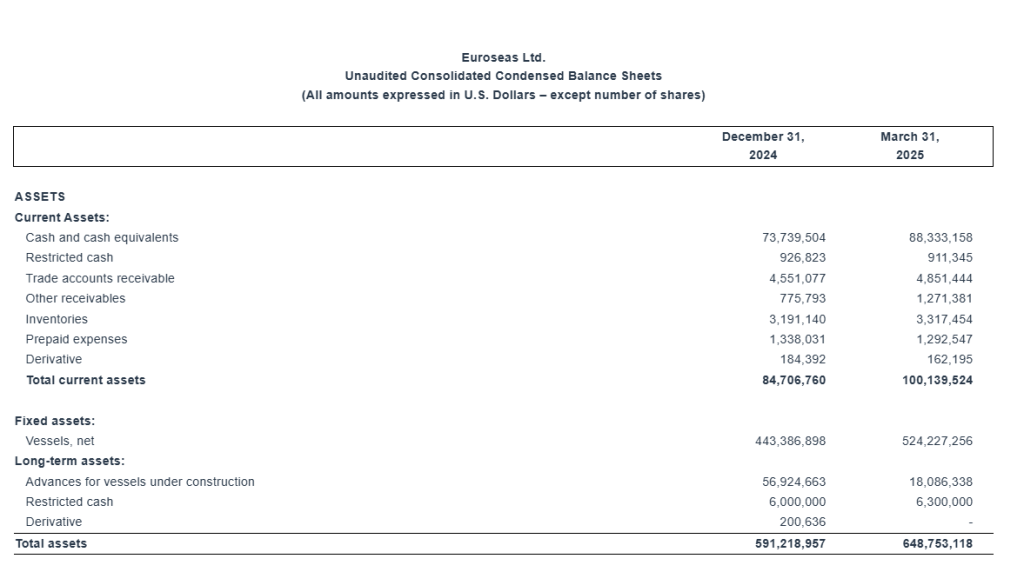
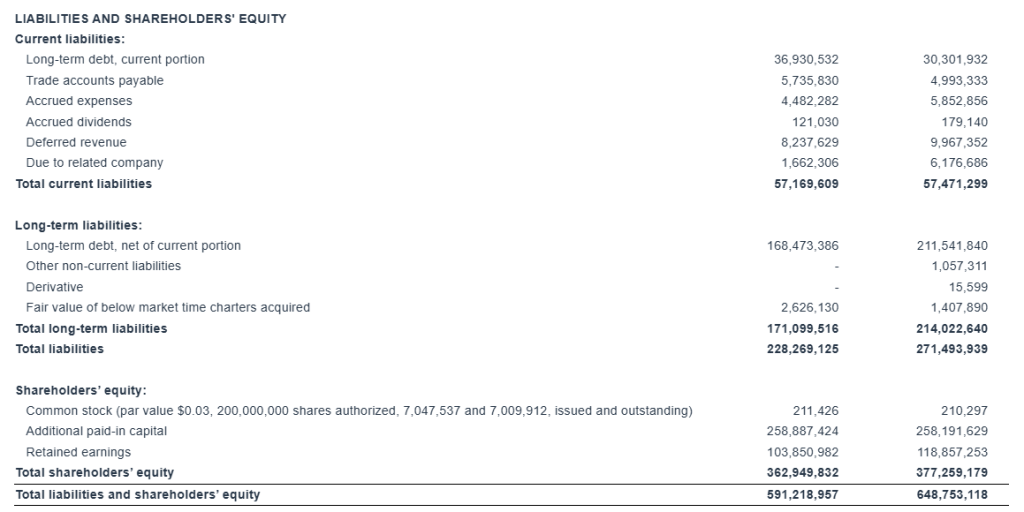
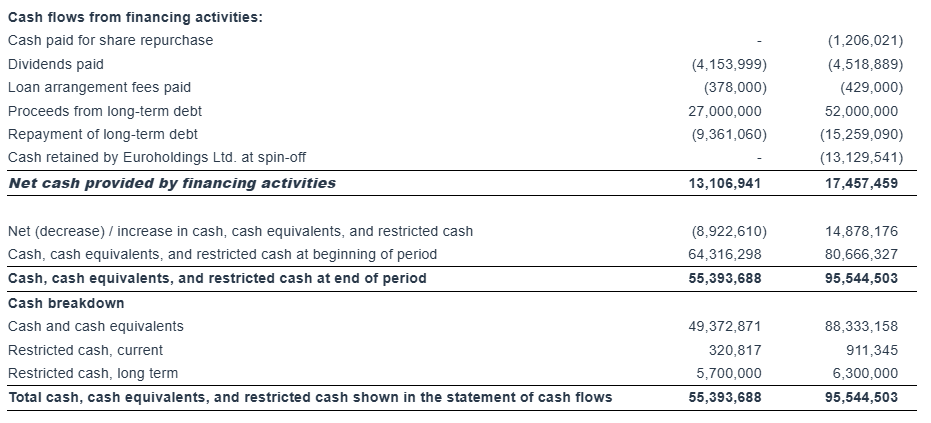
“As of March 31, 2025, our outstanding bank debt (before deducting the unamortized loan fees) was $244.0 million, versus restricted and unrestricted cash of approximately $95.5 million. As of the same date, our scheduled debt repayments over the next 12 months amounted to about $30.7 million (excluding the unamortized loan fees).”
First Quarter 2025 Results:
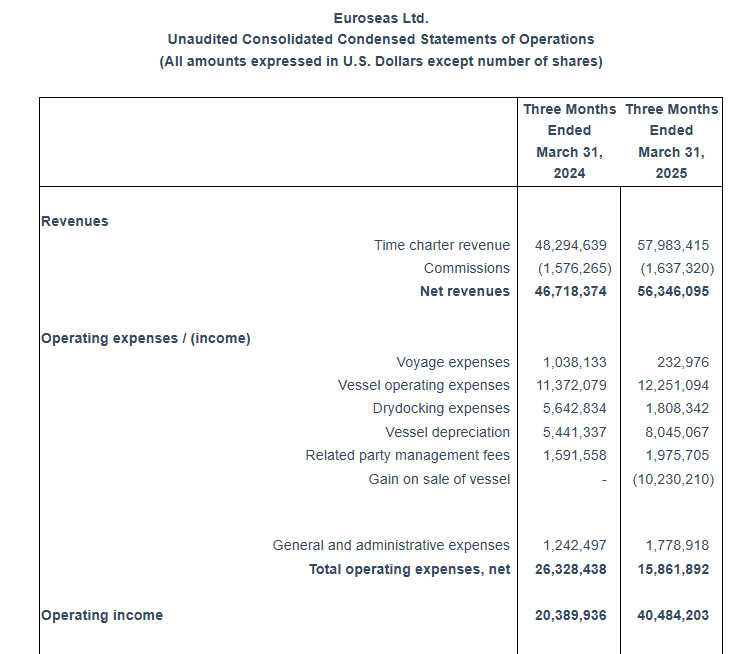
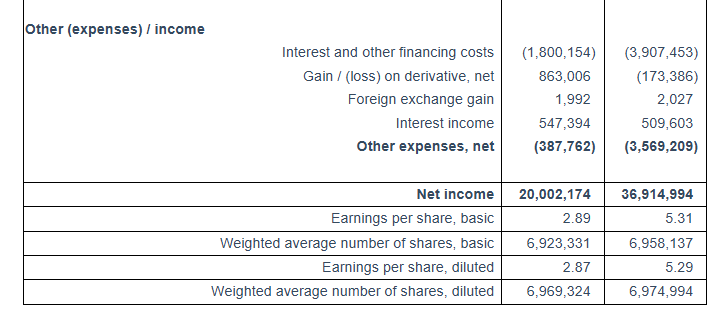
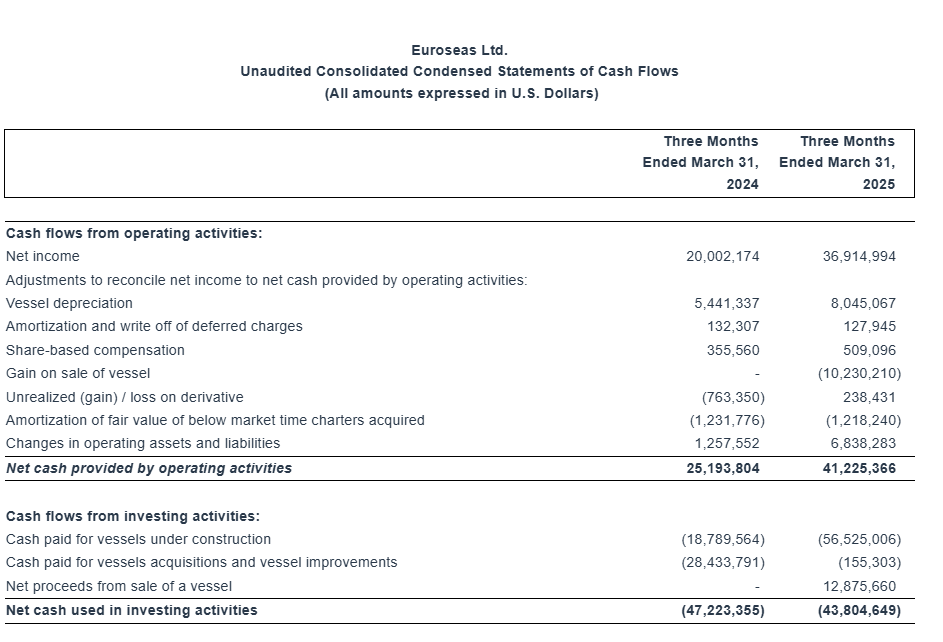
For the first quarter of 2025, the Company reported total net revenues of $56.3 million representing an 20.6% increase over total net revenues of $46.7 million during the first quarter of 2024. On average, 23.68 vessels were owned and operated during the first quarter of 2025 earning an average time charter equivalent rate of $27,563 per day compared to 19.60 vessels in the same period of 2024 earning on average $27,806 per day. The Company reported a net income for the period of $36.9 million, as compared to a net income of $20.0 million for the first quarter of 2024.
Voyage expenses for the first quarter of 2025 amounted to $0.2 million as compared to voyage expenses of $1.0 million for the same period of 2024. The increased amount of 2024 is mainly attributable to bunkers consumption by three of our vessels (M/V “Synergy Antwerp”, M/V “Synergy Oakland” and M/V “Marcos”) during their drydock period.
Vessel operating expenses for the first quarter of 2025 amounted to $12.3 million as compared to $11.4 million for the same period of 2024. The increased amount is due to the higher number of vessels owned and operated in the first quarter of 2025 compared to the corresponding period of 2024.
Depreciation expense for the first quarter of 2025 amounted to $8.0 million compared to $5.4 million for the same period of 2024 due to the increased number of vessels in the Company’s fleet.
Related party management fees for the first quarter of 2025 increased to $2.0 million from $1.6 million for the same period of 2024 as a result of the higher number of vessels in our fleet and the adjustment for inflation in the daily vessel management fee, effective from January 1, 2025, increasing it from 810 Euros to 840 Euros.
In the first quarter of 2025 two of our vessels completed extensive repairs afloat for a total cost of $1.8 million. In the first quarter of 2024 three of our vessels completed their special survey with drydock for a total cost of $5.6 million.
General and administrative expenses slightly increased to $1.8 million in the first quarter of 2025, as compared to $1.2 million in the first quarter of 2024 due to increased professional fees and increased cost for our stock incentive plan.
Interest and other financing costs for the first quarter of 2025 amounted to $3.9 million. Capitalized interest charged on the cost of our newbuilding program was $0.1 million for the first quarter of 2025. For the same period of 2024 interest and other financing costs amounted $1.8 million and the capitalized interest charged on the cost of our newbuilding program was $1.4 million. This increase is due to the increased amount of debt in the current period compared to the same period of 2024. For the three months ended March 31, 2025 the Company recognized a $0.17 million loss on its interest rate swap contract, comprising a $0.07 million realized gain and a $0.24 million unrealized loss. For the three months ended March 31, 2024 the Company recognized a $0.86 million gain on its interest rate swap contracts, comprising a $0.10 million realized gain and a $0.76 million unrealized gain.
Adjusted EBITDA1 for the first quarter of 2025 was $37.1 million, compared to $24.6 million achieved for the first quarter of 2024, primarily higher revenues due to the higher number of vessels owned and operated.
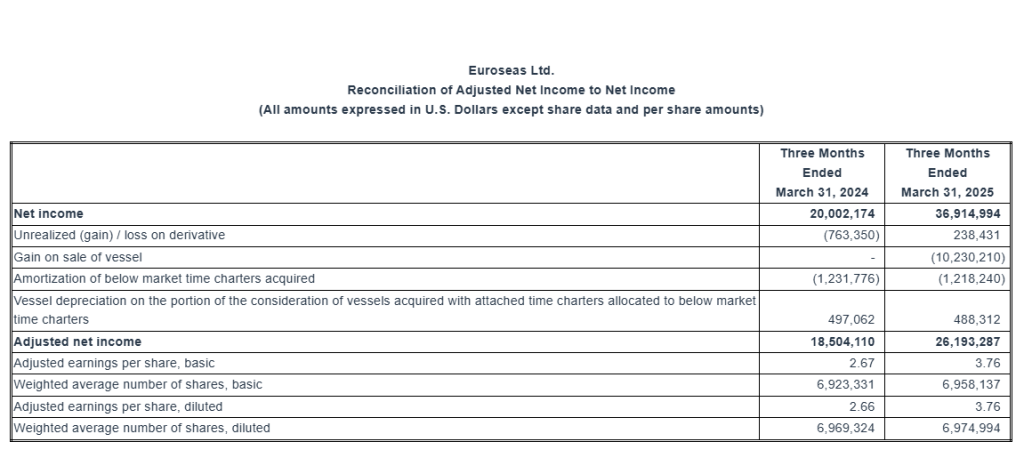
Basic and diluted earnings per share for the first quarter of 2025 was $5.31 and $5.29, respectively, calculated on 6,958,137 basic and 6,974,994 diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding compared to basic and diluted earnings per share of $2.89 and $2.87, respectively for the first quarter of 2024, calculated on 6,923,331 basic and 6,969,324 diluted weighted average number of shares outstanding.
The adjusted earnings per share for the quarter ended March 31, 2025 would have been $3.76 per share basic and diluted, respectively, compared to adjusted earnings of $2.67 and $2.66 per share basic and diluted, respectively, for the first quarter of 2024. Usually, security analysts include Adjusted Net Income in their determination of published estimates of earnings per share.
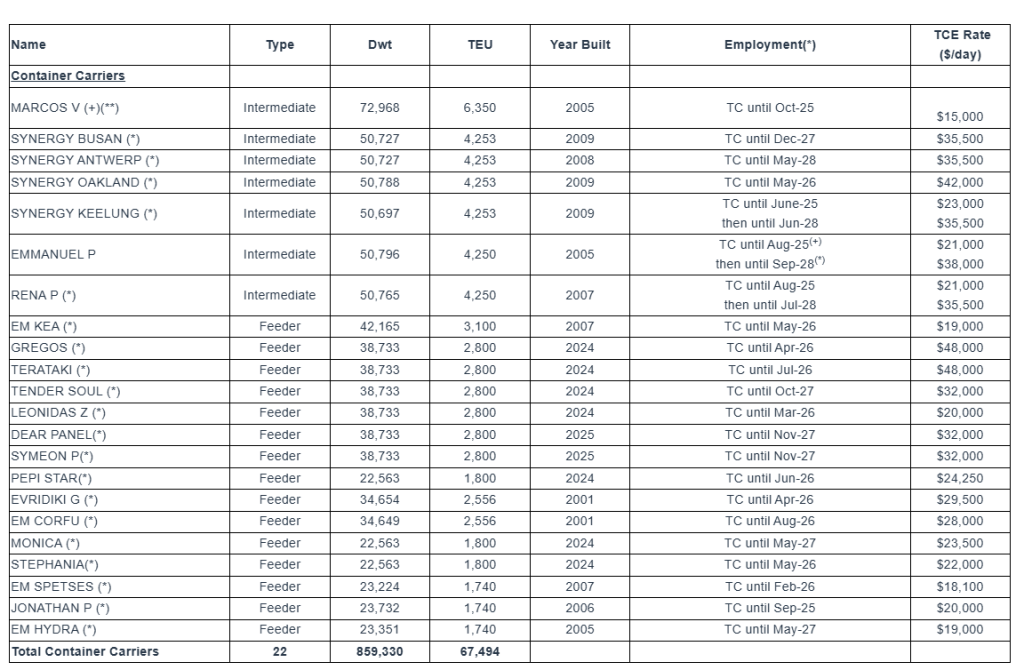
Fleet Profile:
The Euroseas Ltd. fleet profile as of June 18, 2025 is as follows:
Summary Fleet Data:
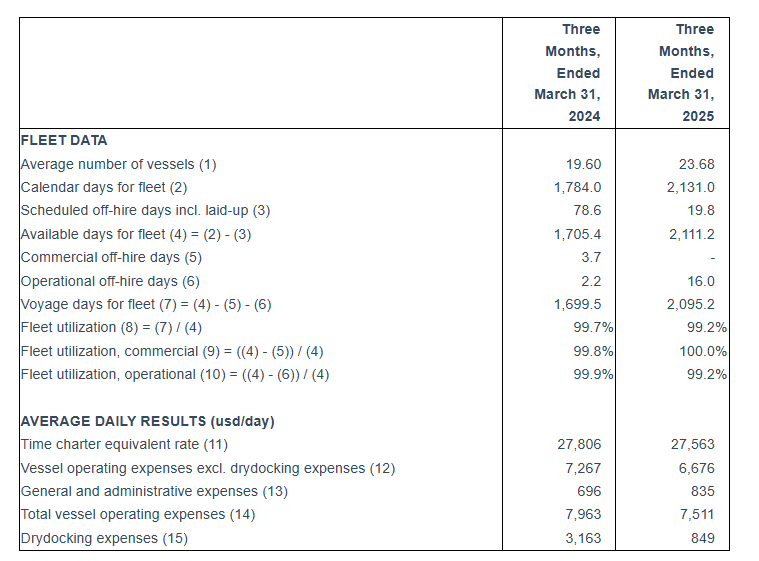
(1) Average number of vessels is the number of vessels that constituted the Company’s fleet for the relevant period, as measured by the sum of the number of calendar days each vessel was a part of the Company’s fleet during the period divided by the number of calendar days in that period.
(2) Calendar days. We define calendar days as the total number of days in a period during which each vessel in our fleet was in our possession including off-hire days associated with major repairs, drydockings or special or intermediate surveys or days of vessels in lay-up. Calendar days are an indicator of the size of our fleet over a period and affect both the amount of revenues and the amount of expenses that we record during that period.
(3) The scheduled off-hire days including vessels laid-up, vessels committed for sale or vessels that suffered unrepaired damages, are days associated with scheduled repairs, drydockings or special or intermediate surveys or days of vessels in lay-up, or vessels that were committed for sale or suffered unrepaired damages.
(4) Available days. We define available days as the Calendar days in a period net of scheduled off-hire days as defined above. We use available days to measure the number of days in a period during which vessels were available to generate revenues.
(5) Commercial off-hire days. We define commercial off-hire days as days a vessel is idle without employment.
(6) Operational off-hire days. We define operational off-hire days as days associated with unscheduled repairs or other off-hire time related to the operation of the vessels.
(7) Voyage days. We define voyage days as the total number of days in a period during which each vessel in our fleet was in our possession net of commercial and operational off-hire days. We use voyage days to measure the number of days in a period during which vessels actually generate revenues or are sailing for repositioning purposes.
(8) Fleet utilization. We calculate fleet utilization by dividing the number of our voyage days during a period by the number of our available days during that period. We use fleet utilization to measure a company’s efficiency in finding suitable employment for its vessels and minimizing the amount of days that its vessels are off-hire for reasons such as unscheduled repairs or days waiting to find employment.
(9) Fleet utilization, commercial. We calculate commercial fleet utilization by dividing our available days net of commercial off-hire days during a period by our available days during that period.
(10) Fleet utilization, operational. We calculate operational fleet utilization by dividing our available days net of operational off-hire days during a period by our available days during that period.
(11) Time charter equivalent rate, or TCE, is a measure of the average daily net revenue performance of our vessels. Our method of calculating TCE is determined by dividing time charter revenue and voyage charter revenue, if any, net of voyage expenses by voyage days for the relevant time period. Voyage expenses primarily consist of port, canal and fuel costs that are unique to a particular voyage, which would otherwise be paid by the charterer under a time charter contract, or are related to repositioning the vessel for the next charter. TCE, which is a non-GAAP measure, provides additional meaningful information in conjunction with voyage revenues, the most directly comparable GAAP measure, because it assists our management in making decisions regarding the deployment and use of our vessels and because we believe that it provides useful information to investors regarding our financial performance. TCE is a standard shipping industry performance measure used primarily to compare period-to-period changes in a shipping company’s performance despite changes in the mix of charter types (i.e., spot voyage charters, time charters and bareboat charters) under which the vessels may be employed between the periods. Our definition of TCE may not be comparable to that used by other companies in the shipping industry.
(12) We calculate daily vessel operating expenses, which includes crew costs, provisions, deck and engine stores, lubricating oil, insurance, maintenance and repairs and related party management fees by dividing vessel operating expenses and related party management fees by fleet calendar days for the relevant time period. Drydocking expenses are reported separately.
(13) Daily general and administrative expenses are calculated by us by dividing general and administrative expenses by fleet calendar days for the relevant time period.
(14) Total vessel operating expenses, or TVOE, is a measure of our total expenses associated with operating our vessels. TVOE is the sum of vessel operating expenses, related party management fees and general and administrative expenses; drydocking expenses are not included. Daily TVOE is calculated by dividing TVOE by fleet calendar days for the relevant time period.
(15) Daily drydocking expenses is calculated by us by dividing drydocking expenses by the fleet calendar days for the relevant period, Drydocking expenses include expenses during drydockings that would have been capitalized and amortized under the deferral method. Drydocking expenses could vary substantially from period to period depending on how many vessels underwent drydocking during the period. The Company expenses drydocking expenses as incurred.
Conference Call and Webcast:
Today, Wednesday, June 18, 2025 at 09:30 a.m. Eastern Time, the Company’s management will host a conference call and webcast to discuss the results.
Conference Call details:
Participants should dial into the call 10 minutes before the scheduled time using the following numbers: 877 405 1226 (US Toll-Free Dial In) or +1 201 689 7823 (US and Standard International Dial In). Please quote “Euroseas” to the operator and/or conference ID 13754421. Click here for additional participant International Toll -Free access numbers.
Alternatively, participants can register for the call using the call me option for a faster connection to join the conference call. You can enter your phone number and let the system call you right away. Click here for the call me option.
Audio Webcast – Slides Presentation:
There will be a live and then archived webcast of the conference call and accompanying slides, available on the Company’s website. To listen to the archived audio file, visit our website http://www.euroseas.gr and click on Company Presentations under our Investor Relations page. Participants to the live webcast should register on the website approximately 10 minutes prior to the start of the webcast.
The slide presentation for the first quarter ended March 31, 2025, will also be available in PDF format minutes prior to the conference call and webcast, accessible on the company’s website (www.euroseas.gr) on the webcast page. Participants to the webcast can download the PDF presentation.
Adjusted EBITDA Reconciliation:
Euroseas Ltd. considers Adjusted EBITDA to represent net income before interest and other financing costs, income taxes, depreciation, (gain) / loss on interest rate swap derivative, net, gain on sale of vessel, and amortization of fair value of below market time charters acquired. Adjusted EBITDA does not represent and should not be considered as an alternative to net income, as determined by United States generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP. Adjusted EBITDA is included herein because it is a basis upon which the Company assesses its financial performance and liquidity position and because the Company believes that this non-GAAP financial measure assists our management and investors by increasing the comparability of our performance from period to period by excluding the potentially disparate effects between periods of financial costs, loss / (gain) on interest rate swaps, gain on sale of vessel, depreciation, and amortization of below market time charters acquired. The Company’s definition of Adjusted EBITDA may not be the same as that used by other companies in the shipping or other industries.
Adjusted net income and Adjusted earnings per share Reconciliation:
Euroseas Ltd. considers Adjusted net income to represent net income before unrealized (gain) / loss on derivative, gain on sale of vessel, amortization of below market time charters acquired and vessel depreciation on the portion of the consideration of vessels acquired with attached time charters allocated to below market time charters. Adjusted net income and Adjusted earnings per share are included herein because we believe they assist our management and investors by increasing the comparability of the Company’s fundamental performance from period to period by excluding the potentially disparate effects between periods of the aforementioned items, which may significantly affect results of operations between periods.
Adjusted net income and Adjusted earnings per share do not represent and should not be considered as an alternative to net income or earnings per share, as determined by GAAP. The Company’s definition of Adjusted net income and Adjusted earnings per share may not be the same as that used by other companies in the shipping or other industries. Adjusted net income and Adjusted earnings per share are not adjusted for all non-cash income and expense items that are reflected in our statement of cash flows.
About Euroseas Ltd.
Euroseas Ltd. was formed on May 5, 2005 under the laws of the Republic of the Marshall Islands to consolidate the ship owning interests of the Pittas family of Athens, Greece, which has been in the shipping business over the past 140 years. Euroseas trades on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the ticker ESEA.
Euroseas operates in the container shipping market. Euroseas’ operations are managed by Eurobulk Ltd., an ISO 9001:2008 and ISO 14001:2004 certified affiliated ship management company, which is responsible for the day-to-day commercial and technical management and operations of the vessels. Euroseas employs its vessels on spot and period charters and through pool arrangements.
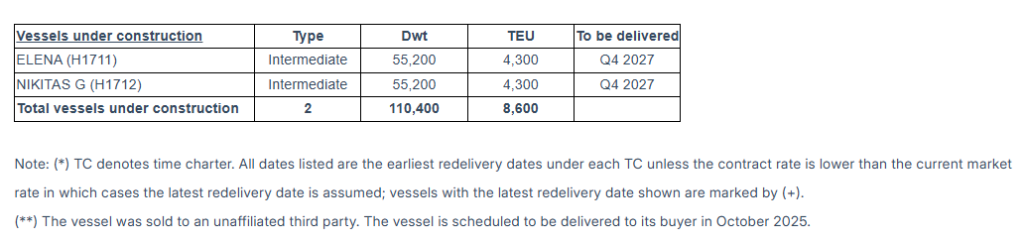
The Company has a fleet of 22 vessels, including 15 Feeder containerships and 7 Intermediate containerships. Euroseas 22 containerships have a cargo capacity of 67,494 teu. After the delivery of two intermediate containership newbuildings in the fourth quarter of 2027, Euroseas’ fleet will consist of 24 vessels with a total carrying capacity of 76,094 teu.
Forward Looking Statement
This press release contains forward-looking statements (as defined in Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) concerning future events and the Company’s growth strategy and measures to implement such strategy; including expected vessel acquisitions and entering into further time charters. Words such as “expects,” “intends,” “plans,” “believes,” “anticipates,” “hopes,” “estimates,” and variations of such words and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Although the Company believes that the expectations reflected in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, no assurance can be given that such expectations will prove to have been correct. These statements involve known and unknown risks and are based upon a number of assumptions and estimates that are inherently subject to significant uncertainties and contingencies, many of which are beyond the control of the Company. Actual results may differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially include, but are not limited to changes in the demand for containerships, competitive factors in the market in which the Company operates; risks associated with operations outside the United States; and other factors listed from time to time in the Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. The Company expressly disclaims any obligations or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to any forward-looking statements contained herein to reflect any change in the Company’s expectations with respect thereto or any change in events, conditions or circumstances on which any statement is based.
Visit the Company’s website www.euroseas.gr
| Company Contact | Investor Relations / Financial Media |
| Tasos Aslidis Chief Financial Officer Euroseas Ltd. 11 Canterbury Lane, Watchung, NJ 07069 Tel. (908) 301-9091 E-mail: mailto:aha@euroseas.gr | Nicolas Bornozis Markella Kara Capital Link, Inc. 230 Park Avenue, Suite 1540 New York, NY 10169 Tel. (212) 661-7566 E-mail: euroseas@capitallink.com |
















































