What’s a ‘Gig’ Job? How it’s Legally Defined Affects Workers’ Rights and Protections
The “gig” economy has captured the attention of technology futurists, journalists, academics and policymakers.
“Future of work” discussions tend toward two extremes: breathless excitement at the brave new world that provides greater flexibility, mobility and entrepreneurial energy, or dire accounts of its immiserating impacts on the workers who labor beneath the gig economy’s yoke.
This article was republished with permission from The Conversation, a news site dedicated to sharing ideas from academic experts. It represents the research-based findings and thoughts of David Weil, Visiting Senior Faculty Fellow, Ash Center for Democracy Harvard Kennedy School / Professor, Heller School for Social Policy and Management, Brandeis University.
These widely diverging views may be partly due to the many definitions of what constitutes “gig work” and the resulting difficulties in measuring its prevalence. As an academic who has studied workplace laws for decades and ran the federal agency that enforces workplace protections during the Obama administration, I know the way we define, measure and treat gig workers under the law has significant consequences for workers. That’s particularly true for those lacking leverage in the labor market.
While there are benefits for workers for this emerging model of employment, there are pitfalls as well. Confusion over the meaning and size of the gig workforce – at times the intentional work of companies with a vested economic interest – can obscure the problems gig status can have on workers’ earnings, workplace conditions and opportunities.
Defining Gig Work
Many trace the phrase “gig economy” to a 2009 essay in which editor and author Tina Brown proclaimed: “No one I know has a job anymore. They’ve got Gigs.”
Although Brown focused on professional and semiprofessional workers chasing short-term work, the term soon applied to a variety of jobs in low-paid occupations and industries. Several years later, the rapid ascent of Uber, Lyft and DoorDash led the term gig to be associated with platform and digital business models. More recently, the pandemic linked gig work to a broader set of jobs associated with high turnover, limited career prospects, volatile wages and exposure to COVID-19 uncertainties.
The imprecision of gig, therefore, connotes different things: Some uses focus on the temporary or “contingent” nature of the work, such as jobs that may be terminated at any time, usually at the discretion of the employer. Other definitions focus on the unpredictability of work in terms of earnings, scheduling, hours provided in a workweek or location. Still other depictions focus on the business structure through which work is engaged – a staffing agency, digital platform, contractor or other intermediary. Further complicating the definition of gig is whether the focus is on a worker’s primary source of income or on side work meant to supplement income.
Measuring Gig Work
These differing definitions of gig work have led to widely varying estimates of its prevalence.
A conservative estimate from the Bureau of Labor Statistics household-based survey of “alternative work arrangements” suggests that gig workers “in non-standard categories” account for about 10% of employment. Alternatively, other researchers estimate the prevalence as three times as common, or 32.5%, using a Federal Reserve survey that broadly defines gig work to include any work that is temporary and variable in nature as either a primary or secondary source of earnings. And when freelancing platform Upworks and consulting firm McKinsey & Co. use a broader concept of “independent work,” they report rates as high as 36% of employed respondents.
No consensus definition or measurement approach has emerged, despite many attempts, including a 2020 panel report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Various estimates do suggest several common themes, however: Gig work is sizable, present in both traditional and digital workplaces, and draws upon workers across the age, education, demographic and skill spectrum.
Why it Matters
As the above indicates, gig workers can range from high-paid professionals working on a project-to-project basis to low-wage workers whose earnings are highly variable, who work in nonprofessional or semiprofessional occupations and who accept – by choice or necessity – volatile hours and a short-term time commitment from the organization paying for that work.
Regardless of their professional status, many workers operating in gig arrangements are classified as independent contractors rather than employees. As independent contractors, workers lose rights to a minimum wage, overtime and a safe and healthy work environment as well as protections against discrimination and harassment. Independent contractors also lose access to unemployment insurance, workers’ compensation and paid sick leave now required in many states.
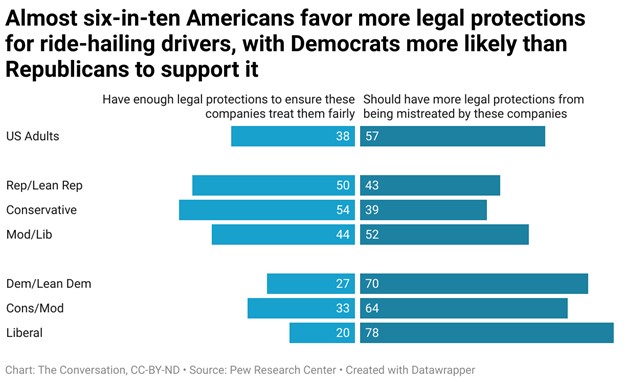
Federal and state laws differ in the factors they draw on to make that call. A key concept underlying that determination is how “economically dependent” the worker is on the employer or contracting party. Greater economic independence – for example, the ability to determine price of service, how and where tasks are done and opportunities for expanding or contracting that work based on the individual’s own skills, abilities and enterprise – suggest a role as an independent contractor.
In contrast, if the hiring party basically calls the shots – for example, controlling what the individual does, how they do their work and when they do it, what they are permitted to do and not do, and what performance is deemed acceptable – this suggests employee status. That’s because workplace laws are generally geared toward employees and seek to protect workers who have unequal bargaining leverage in the labor market, a concept based on long-standing Supreme Court precedent.
Making Work More Precarious
Over the past few decades, a growing number of low-wage workers find themselves in gig work situations – everything from platform drivers and delivery personnel to construction laborers, distribution workers, short-haul truck drivers and home health aides. Taken together, the grouping could easily exceed 20 million workers.
Many companies have incentives to classify these workers as independent contractors in order to reduce costs and risks, not because of a truly transformed nature of work where those so classified are real entrepreneurs or self-standing businesses.
Since gig work tends to be volatile and contingent, losing employment protections amplifies the precariousness of work. A business using misclassified workers can gain cost advantages over competitors who treat their workers as employees as required by the law. This competitive dynamic can spread misclassification to new companies, industries and occupations – a problem we addressed directly, for example, in construction cases when I led the Wage and Hour Division and more recently in several health care cases.
The future of work is not governed by immutable technological forces but involves volitional private and public choices. Navigating to that future requires weighing the benefits gig work can provide some workers with greater economic independence against the continuing need to protect and bestow rights for the many workers who will continue to play on a very uneven playing field in the labor market.