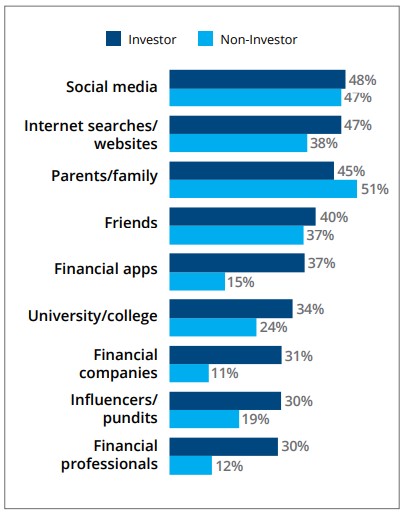
Is the Fed Falling Behind on Slowing the Economy?
Is the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy losing out to inflationary pressures? While supply chain costs have long been taken out of the inflation forecast, demand pressures have been stronger than hoped for by the Fed. One area of demand is the labor markets. While the Federal Reserve has a dual mandate to keep prices stable and maximize employment, the shortage of workers is adding to demand-pull inflation as wages are a large input cost in a service economy. As employment remains strong, they have room to raise rates, but if strong employment is a significant cause of price pressures, they may decide to keep the increases coming.
Background
The number of new jobs unfilled increased last month as US job openings rose unexpectedly in April. The total job openings stood at 10.1 million. Make no mistake, the members of the Fed trying to steer this huge economic ship would like to see everyone working. However, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reporting “unemployed persons” at 5.7 million in April as compared to 10.1 million job openings, creates far more demand than there are people to fill the positions. Those with the right skills will find their worth has climbed as they get bid up by employers that are still financially better off hiring more expensive talent rather than doing without.
This causes wage inflation as these increased business costs work their way down into the final cost of goods and services we consume, as inflation.
Where We’re At
The 10.1 million job openings employers posted is an increase from the 9.7 million in the prior month. It is also the most since January 2023. In contrast, economists had expected vacancies to slip below 9.5 million. The increase and big miss by economists’ forecasting increases in job opportunities is a clear sign of strength in the nation’s labor market. This complicates Chair Jerome Powell’s position, along with other Fed members.
It isn’t popular to try to crush demand for new employees, but rising consumer costs at more than twice the Fed’s target will be viewed as too much.
The Fed says that it is data driven, this data is unsettling for those hoping for a pause or pivot.
The Investment Climate
These numbers and other strong economic numbers that were reported in April, create some uncertainty for investors as most would prefer to see the Fed stimulating rather than tightening conditions.
But the market has been resilient, despite the Feds’ resolve. The Fed has raised its benchmark interest rate ten times in the last 14 months. Yet jobs remain unfilled, and the stock market has gained quite a bit of ground in 2023. The concern has been that the Fed may overdo it and cause a recession. While even the Fed Chair admitted this is a risk he is willing to take, he also added that it is easier to start a stalled economy than it is to reel one in and the inflation that goes along with expansion.
So the strong labor market (along with other recent data releases) provides room for the Fed to tighten as there are still nearly two jobs for every job seeker. Additional tightening will eventually have the effect of simmering inflation to a more tolerable temperature. If the Fed overdoes it on the brake pedal, according to Powell, he knows where the gas pedal is.
Managing Editor, Channelchek
Sources