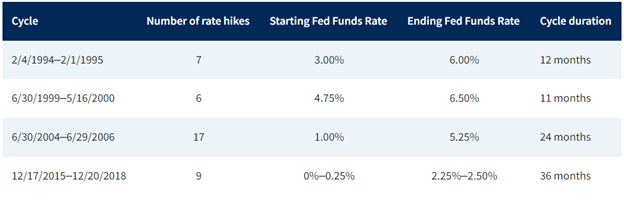
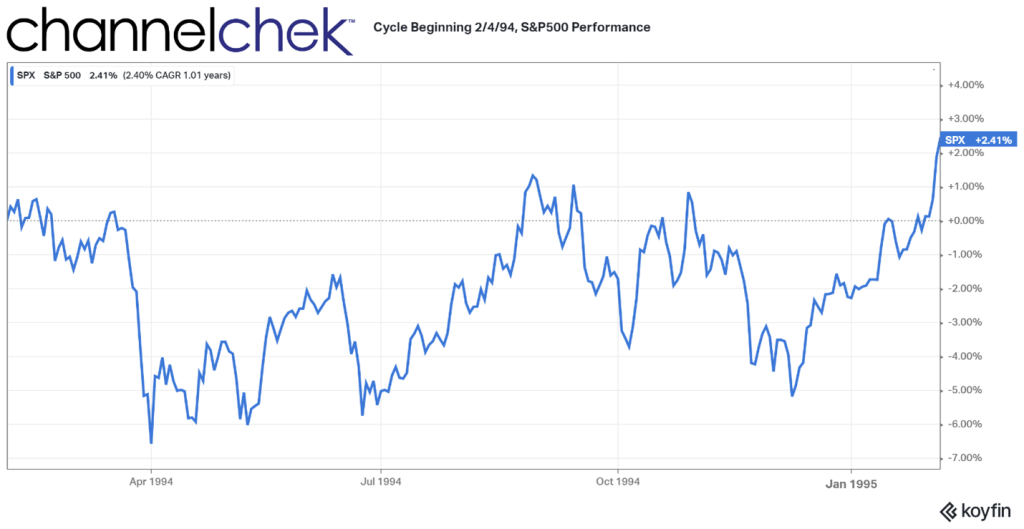
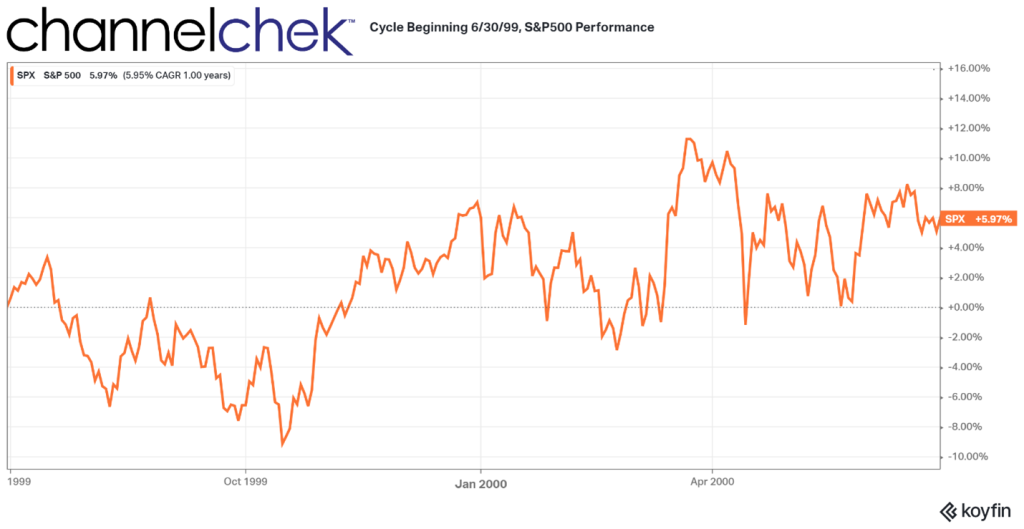
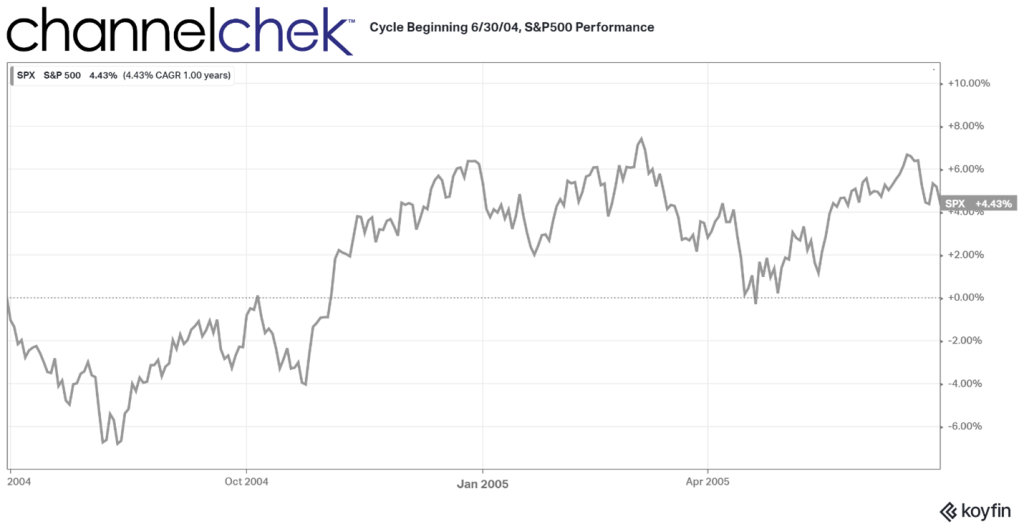
The Federal Reserve held its benchmark interest rate unchanged on Wednesday following its latest two-day policy meeting. However, the central bank signaled that multiple rate cuts are likely before the end of 2024 as it continues efforts to bring down stubbornly high inflation.
In its post-meeting statement, the Fed kept the target range for its federal funds rate at 5.25%-5.5%, where it has been since last July. This matched widespread expectations among investors and economists.
The more notable part of today’s announcements came from the Fed’s updated Summary of Economic Projections. The anonymous “dot plot” of individual policymaker expectations showed a median projection for three quarter-point rate cuts by year-end 2024.
This would mark a pivotal shift for the Fed, which has been steadily raising rates over the past year at the fastest pace since the 1980s to combat surging inflation. The last time the central bank cut rates was in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic in March 2020.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell and other officials have signaled in recent months that softer policies could be appropriate once inflation shows further clear signs of moderating. Consumer prices remain elevated at 6% year-over-year as of February.
“While inflation has moderated somewhat since the middle of last year, it remains too high and further progress is needed,” said Powell in his post-meeting press conference. “We will remain data-dependent as we assess the appropriate stance of policy.”
The Fed’s updated economic projections now forecast GDP growth of 2.1% in 2024, up sharply from the 1.4% estimate in December. Core inflation is seen decelerating to 2.6% by year-end before returning to the Fed’s 2% target by 2026. The unemployment rate projection was nudged down to 4%.
With economic conditions still relatively strong, Powell stressed the central bank’s ability to move gradually and in a “risk management” mindset on raising or lowering interest rates. Markets expect the first rate cut to come as soon as June.
“The process of getting inflation down to 2% has a long way to go and is likely to be bumpy,” said Powell. “We have more work to do.”
The potential for rate cuts this year hinges on how quickly the lagging effects of the Fed’s aggressive tightening campaign over the past year feed through into lower price pressures. Policymakers will be closely watching metrics like consumer spending, wage growth, supply chains and inflation expectations for any signs that demand is cooling sustainably.
So far, the labor market has remained resilient, with job gains still robust and the unemployment rate hovering near 50-year lows around 3.5%. This tightness has allowed for solid wage gains, which risks perpetuating an inflationary price-wage spiral if not brought to heel.
While the road ahead remains highly uncertain, Powell stated that he feels the Fed has made enough policy adjustments already to at least pause the rate hiking cycle for now and switch into a data-driven risk management mode. This allows officials to be “patient” and avoid over-tightening while monitoring incoming information.
The Fed Chair also noted that discussions on reducing the central bank’s $8.4 trillion balance sheet began at this meeting, but no decisions have been made yet on adjusting the current runoff caps or pace.
In all, today’s Fed meeting reiterated the central bank’s intention to keep rates elevated for now while laying the groundwork for an eventual pivot to easier policy sometime later this year as disinflationary forces take deeper hold. Striking that balance between under and overtightening will be key for engineering a long-awaited soft landing for the economy.