Old School Versus New School are your Investments Inline with the Changing Investor Makeup?
Investing tastes and strategies vary by generation. And as technologies advance and provide self-directed investors with new methodologies, all investors should pay attention to shifts in the marketplace. According to a report by APEX Fintech Solutions, millennials, and Gen Z are gaining wealth at a rate of 25%, while all generations increased at only 16%. There are major implications for market moves as trillions are controlled by those that may have different risk tolerance, different holding periods, or a broadly different knowledge base about many companies and their products.
What Was Measured
The data compiled in the APEX report analyzed more than 1.3 million Gen Z accounts, in addition to
over 4.0 million millennial accounts, 2.0 million held by Gen X, and over half a million baby boomers. The numbers are calculated as of December 31, 2022. It also compared managed accounts to self-directed investments.
The four generations were defined in this way:
Z: Born 1997-2012 (25 and younger) – Generation Z
M: Born 1981-1996 (26-41 years old) – Millenials
X: Born 1965-1980 (42-57 years old) – Generation X
B: Born 1946-1964 (58-76 years old) – Baby Boomers
Notable Investment Trends and Differences
Sifting through the stats (Q1 2020 – Q2 2022) and comparing self-directed investors with professionally managed accounts, self-directed, as a whole, did comparatively little selling at the lows of the stock market during the pandemic-inspired sell-off (early 2020). Instead, the peak in selling (the low for the hold rate) for self-directed accounts came at the height of meme stock and market run-up in Q1 2021. Over the period, including when selling was at its peak, managed accounts consistently were more active, changing and adding to positions at a much higher rate. Self-directed portfolios were more likely to enter a position, hold it and at times add to current positions.

Late 2022 Comparisons
During the last quarter of 2022, the most popular stocks held by all generations remained the same while the companies positioned in the remainder of the account holdings were in flux and altered quite a bit. The top stocks held were Tesla (TSLA), Apple Inc. (AAPL), Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN) and Microsoft Corp (MSFT); these were core holdings that were barely traded by any generational grouping.
Below these holdings, each generation had different sets of significant shifts, with real estate investment trusts growing for all four generational groups. Industrials and Energy Sectors were also favored across generations, while holdings in service-related industries were reduced. The two strongest performing sectors in Q4, across the generational rankings, were industrials and energy.
Across all generational holdings, industrials were led by General Electric (GE), Lockheed Martin Corp (LMT), Raytheon Technologies Corp (RTX), Boeing Co (BA), and Delta Air Lines, Inc. (DAL), while energy stocks were led by namely Chevron Corporation (CVX) and Exxon Mobil Corp (XOM), and followed closely by BP plc (BP), Energy Transfer LP Unit (ET), and Enterprise Products Partners LP (EPD).
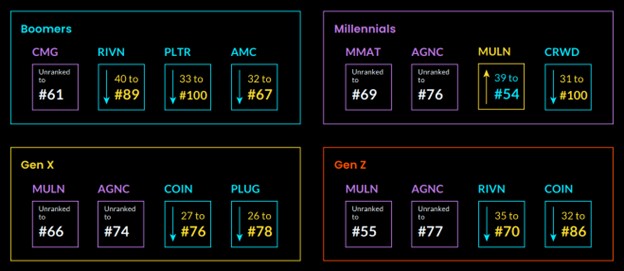
The tickers that dropped the most on the APEX top 100 list included Rivian (RIVN), which dipped an average of 27.8 spots across all generations, followed by AMC, which slipped 11.8 spots lower. For Gen Z, millennials and Gen X they also reduced holdings in TTD , DKNG and RBLX which dropped between 18 to 27 positions lower in the top 100 holdings.
Greatest Rank Changes by Generation
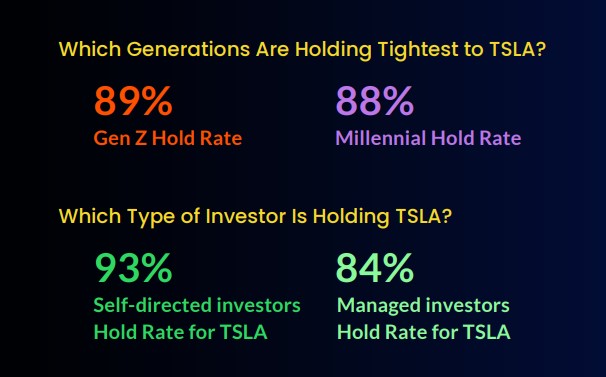
Tesla (TSLA) which had been in the number one position for Gen X and Gen Z, dropped to number two last quarter as Apple (AAPL) regained popularity. TSLA spent nine consecutive quarters in the top spot, all for Gen Z, TSLA had a four-quarter streak. At number two, TSLA is still a popular stock, especially with Millennials and Gen Z, they chose to hold at the highest rates, even as the price plummeted.
For self-directed investors of all ages, the TSLA hold rate is significantly higher (93%) than for investors who use managed brokerage services (84%).
Throughout the fourth quarter of 2022, retail investors displayed a risk-managed approach to trading and strategic investing as they measured recession risks and a changed monetary policy. Millennials were the most active traders in the fourth quarter, the numbers indicate they were engaged and paid attention as market conditions evolved.
Take Away
There are two big takeaways from the study, the first is that retail investors are gaining power and have become savvier and in tune with smart investing.
The second takeaway is related to the first. Since the start of 2020, combined assets for all generations have risen 16% to $52.4 trillion. Two age groupings, millennials and Gen Z, are gaining wealth at a much higher 25% pace. The massive shift in market power is unfolding and has major implications for how, when, and why investments are transacted.
Managing Editor, Channelchek
Source
https://go.apexfintechsolutions.com/hubfs/ANIO/Apex_Q4-2022_ANIO-Report.pdf