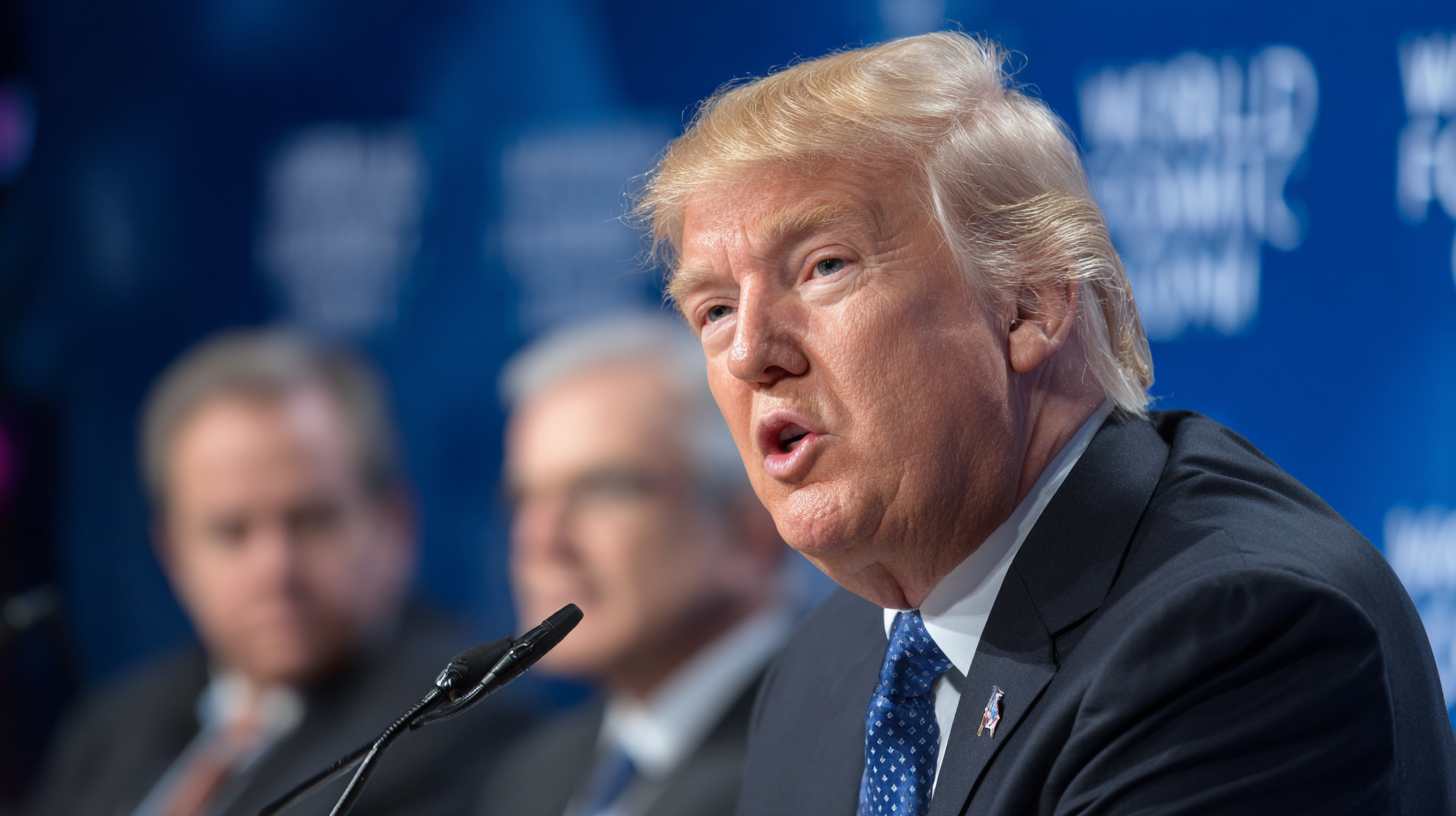
President Donald Trump abruptly reversed course on proposed tariffs against European nations on Wednesday, announcing he would suspend the planned measures after reaching what he described as a “framework of a future deal” related to Greenland and broader Arctic cooperation.
In a post on Truth Social, Trump said the agreement-in-principle followed discussions with NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte and would benefit both the United States and its allies. As a result, the tariffs that were scheduled to take effect on February 1 will no longer move forward, easing market tensions that had flared over the past several days.
“This solution, if consummated, will be a great one for the United States of America, and all NATO Nations,” Trump wrote, adding that further details would be released as negotiations progress.
The announcement marked a sharp shift from Trump’s weekend threat to impose 10% tariffs on eight European countries that he claimed were obstructing U.S. efforts to pursue a deal involving Greenland, with rates set to rise to 25% by June if no agreement was reached. The proposed tariffs would have applied broadly to all goods imported from the affected nations, sparking fears of renewed transatlantic trade conflict.
Those concerns quickly reverberated through financial markets, contributing to volatility as investors weighed the prospect of escalating tariffs between long-standing allies. European leaders responded forcefully, with the European Parliament freezing a ratification vote on a U.S.–EU trade agreement and EU officials reportedly exploring retaliatory tariffs on up to $108 billion worth of American exports.
Trump’s reversal helped stabilize sentiment, at least temporarily, by removing the immediate threat of trade disruption.
The tariff dispute stemmed from Trump’s renewed push for negotiations over Greenland, a Danish territory with growing strategic importance due to its location and natural resources. Speaking earlier Wednesday at the World Economic Forum in Davos, Trump called for “immediate negotiations” while signaling he was ruling out the use of military force.
His comments walked a careful line—pressing European partners for cooperation while stopping short of overt escalation. “You can say yes, and we will be very appreciative, or you can say no, and we will remember,” Trump said, underscoring the pressure campaign that preceded the tariff threats.
While details of the Greenland framework remain scarce, Trump indicated the discussions would extend beyond Greenland itself to include broader Arctic coordination, an area of increasing geopolitical competition.
The episode unfolded against ongoing legal uncertainty surrounding Trump’s global tariff authority. The U.S. Supreme Court has so far declined to issue rulings this year on challenges to the legality and scope of his trade duties, leaving unresolved questions about executive power in trade policy.
Trump said Vice President JD Vance, Secretary of State Marco Rubio, and Special Envoy Steve Witkoff will lead negotiations going forward. He also praised NATO allies for increasing defense spending, a recurring theme in his foreign policy messaging.
For now, the suspension of tariffs offers breathing room for markets and diplomats alike. But with negotiations still incomplete, investors and U.S. allies will be watching closely to see whether the “framework” evolves into a durable agreement—or another flashpoint in an increasingly unpredictable trade landscape.