Zach Winn | MIT News Office
When it comes to battery innovations, much attention gets paid to potential new chemistries and materials. Often overlooked is the importance of production processes for bringing down costs.
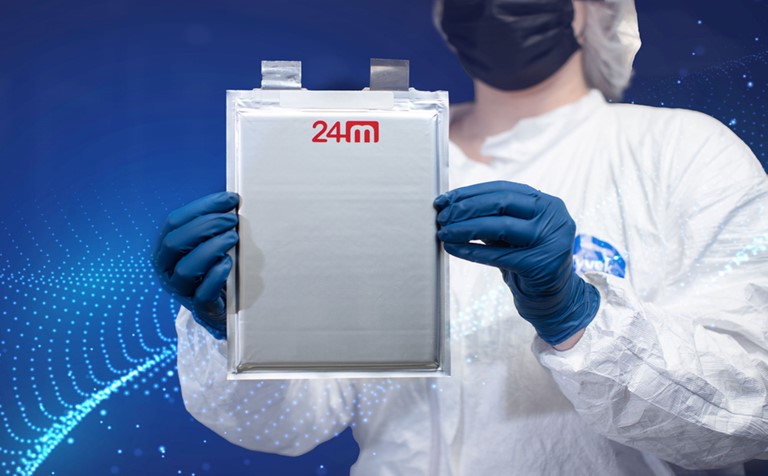
Now the MIT spinout 24M Technologies has simplified lithium-ion battery production with a new design that requires fewer materials and fewer steps to manufacture each cell. The company says the design, which it calls “SemiSolid” for its use of gooey electrodes, reduces production costs by up to 40 percent. The approach also improves the batteries’ energy density, safety, and recyclability.
Judging by industry interest, 24M is onto something. Since coming out of stealth mode in 2015, 24M has licensed its technology to multinational companies including Volkswagen, Fujifilm, Lucas TVS, Axxiva, and Freyr. Those last three companies are planning to build gigafactories (factories with gigawatt-scale annual production capacity) based on 24M’s technology in India, China, Norway, and the United States.
“The SemiSolid platform has been proven at the scale of hundreds of megawatts being produced for residential energy-storage systems. Now we want to prove it at the gigawatt scale,” says 24M CEO Naoki Ota, whose team includes 24M co-founder, chief scientist, and MIT Professor Yet-Ming Chiang.
Establishing large-scale production lines is only the first phase of 24M’s plan. Another key draw of its battery design is that it can work with different combinations of lithium-ion chemistries. That means 24M’s partners can incorporate better-performing materials down the line without substantially changing manufacturing processes.
The kind of quick, large-scale production of next-generation batteries that 24M hopes to enable could have a dramatic impact on battery adoption across society — from the cost and performance of electric cars to the ability of renewable energy to replace fossil fuels.
“This is a platform technology,” Ota says. “We’re not just a low-cost and high-reliability operator. That’s what we are today, but we can also be competitive with next-generation chemistry. We can use any chemistry in the market without customers changing their supply chains. Other startups are trying to address that issue tomorrow, not today. Our tech can address the issue today and tomorrow.”
A Simplified Design
Chiang, who is MIT’s Kyocera Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, got his first glimpse into large-scale battery production after co-founding another battery company, A123 Systems, in 2001. As that company was preparing to go public in the late 2000s, Chiang began wondering if he could design a battery that would be easier to manufacture.
“I got this window into what battery manufacturing looked like, and what struck me was that even though we pulled it off, it was an incredibly complicated manufacturing process,” Chiang says. “It derived from magnetic tape manufacturing that was adapted to batteries in the late 1980s.”
In his lab at MIT, where he’s been a professor since 1985, Chiang started from scratch with a new kind of device he called a “semi-solid flow battery” that pumps liquids carrying particle-based electrodes to and from tanks to store a charge.
In 2010, Chiang partnered with W. Craig Carter, who is MIT’s POSCO Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, and the two professors supervised a student, Mihai Duduta ’11, who explored flow batteries for his undergraduate thesis. Within a month, Duduta had developed a prototype in Chiang’s lab, and 24M was born. (Duduta was the company’s first hire.)
But even as 24M worked with MIT’s Technology Licensing Office (TLO) to commercialize research done in Chiang’s lab, people in the company including Duduta began rethinking the flow battery concept. An internal cost analysis by Carter, who consulted for 24M for several years, ultimately lead the researchers to change directions.
That left the company with loads of the gooey slurry that made up the electrodes in their flow batteries. A few weeks after Carter’s cost analysis, Duduta, then a senior research scientist at 24M, decided to start using the slurry to assemble batteries by hand, mixing the gooey electrodes directly into the electrolyte. The idea caught on.
The main components of batteries are the positive and negatively charged electrodes and the electrolyte material that allows ions to flow between them. Traditional lithium-ion batteries use solid electrodes separated from the electrolyte by layers of inert plastics and metals, which hold the electrodes in place.
Stripping away the inert materials of traditional batteries and embracing the gooey electrode mix gives 24M’s design a number of advantages.
For one, it eliminates the energy-intensive process of drying and solidifying the electrodes in traditional lithium-ion production. The company says it also reduces the need for more than 80 percent of the inactive materials in traditional batteries, including expensive ones like copper and aluminum. The design also requires no binder and features extra thick electrodes, improving the energy density of the batteries.
“When you start a company, the smart thing to do is to revisit all of your assumptions and ask what is the best way to accomplish your objectives, which in our case was simply-manufactured, low-cost batteries,” Chiang says. “We decided our real value was in making a lithium-ion suspension that was electrochemically active from the beginning, with electrolyte in it, and you just use the electrolyte as the processing solvent.”
In 2017, 24M participated in the MIT Industrial Liaison Program’s STEX25 Startup Accelerator, in which Chiang and collaborators made critical industry connections that would help it secure early partnerships. 24M has also collaborated with MIT researchers on projects funded by the Department of Energy.
Enabling the Battery Revolution
Most of 24M’s partners are eyeing the rapidly growing electric vehicle (EV) market for their batteries, and the founders believe their technology will accelerate EV adoption. (Battery costs make up 30 to 40 percent of the price of EVs, according to the Institute for Energy Research).
“Lithium-ion batteries have made huge improvements over the years, but even Elon Musk says we need some breakthrough technology,” Ota says, referring to the CEO of EV firm Tesla. “To make EVs more common, we need a production cost breakthrough; we can’t just rely on cost reduction through scaling because we already make a lot of batteries today.”
24M is also working to prove out new battery chemistries that its partners could quickly incorporate into their gigafactories. In January of this year, 24M received a grant from the Department of Energy’s ARPA-E program to develop and scale a high-energy-density battery that uses a lithium metal anode and semi-solid cathode for use in electric aviation.
That project is one of many around the world designed to validate new lithium-ion battery chemistries that could enable a long-sought battery revolution. As 24M continues to foster the creation of large scale, global production lines, the team believes it is well-positioned to turn lab innovations into ubiquitous, world-changing products.
“This technology is a platform, and our vision is to be like Google’s Android [operating system], where other people can build things on our platform,” Ota says. “We want to do that but with hardware. That’s why we’re licensing the technology. Our partners can use the same production lines to get the benefits of new chemistries and approaches. This platform gives everyone more options.”
Reprinted with permission of MIT News ( http://news.mit.edu/)