Inflation Still Surprisingly Strong and Economy Weak
Two important numbers were released on the last day of September. One was based on old news but significant in its finality; it’s the final revision to GDP for the second quarter. The next is viewed as the Fed’s preferred inflation gauge, the PCE deflator. The final GDP number will make it more difficult for public officials or pundits to suggest we can avoid a recession in 2022, and the second did not give any hope that the Fed will have any reason to change course on tightening.
A Recession By Any Other Name
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the indicator that reflects the amount of output produced quarterly in a country. In the U.S., the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) releases two estimates of quarterly GDP, known as the advance and preliminary estimates, in the two months before the release of the final number. So until the final number prints, the number GDP measure is subject to revision.
On September 30, 2022, the Final GDP report for the second quarter was released by the BEA. The report shows that GDP decreased at an annual rate of 0.6 percent in the second quarter of 2022 (table 1). This decline in economic output follows a decline of 1.6% in the first quarter of 2022.
Do two-quarters of a receding economy, based on GDP, indicate the U.S. is in the recessionary part of the business cycle? Most textbooks would agree with that definition. However, there is a Business Cycle Dating Committee within the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) that determines and labels where the nation is within the economic cycles; they have not made any declaration.
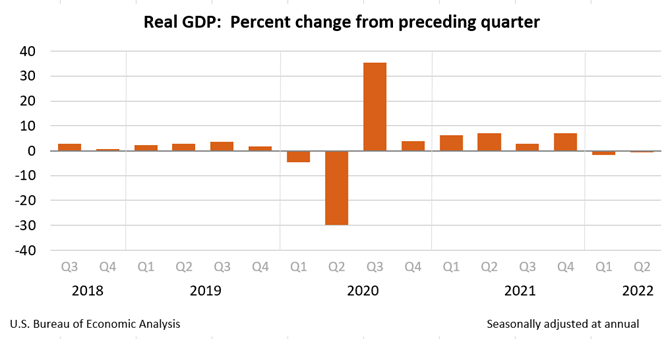
So far, in 2022, the economy has not experienced any economic growth. If the six months of contraction is eventually deemed an official recession, it will thus far have been a shallow one, characterized by strong employment.
Price Increases Higher than Expected
Inflation is still on many investor’s radar. The Fed is targeting reducing inflation to its 2% target. The inflation measure they use for this target is the PCE Deflator. That measure was released this morning, and it validates the aggressive actions being taken by the Federal Reserve. And suggests the Fed has a lot more work to do.
The personal consumption expenditures price index (PCE), which the Fed targets at 2%, rose 6.2% in August from a year earlier, the Commerce Department reported. Underlying inflation, as measured by a core reading that excludes food and energy prices, rose 4.9% from 4.7% previously.
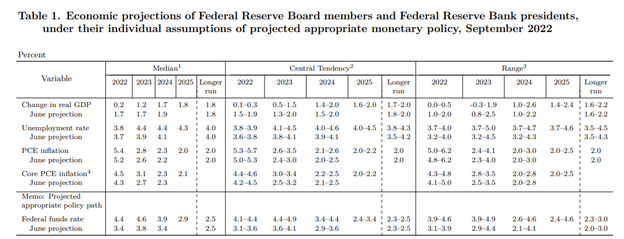
These numbers are well in excess of the Fed’s target and seemingly trending upward. Expectations are the Fed will provide up to another 150 bp increase (1.50%) over the coming months. This would cause the Fed Funds rate to trade near 5%. There is nothing in today’s release that would likely cause expectations to change.
Stagflation?
High inflation and negative growth have many repeating the word “stagflation”. Stagflation has one more element missing, which is high unemployment. The current economic conditions in the U.S. include high demand for workers, this shortage actually helps feed into the inflation the Fed is trying to tame.
Take Away
The economy contracted slightly in the second quarter of 2022. The decline in production was smaller than measured during the first quarter. Federal Reserve policymakers saw one more reason to keep applying the economic brake pedal by taking money out of the economy, increasing upward rate pressures. The Fed caused rates to rise from 40-year lows faster than any time since the 1980s.
Stock market participants are factored into the Fed’s policy only to the extent that market moves may impact inflation or employment. The markets (stocks, bonds, real estate, gold) are negative on the year. There are some who suggest the Fed will use this as a signal to alter policy, if the Fed bowed to any of the markets listed here, the sign of weakness might actually cause a market collapse in stocks and bonds.
Managing Editor, Channelchek
Sources
https://www.bea.gov/news/2022/personal-income-and-outlays-august-2022-and-annual-update
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/fed-seen-keeping-big-rate-131814754.html
https://www.stlouisfed.org/on-the-economy/2014/may/do-revisions-to-gdp-follow-patterns
https://www.learningmarkets.com/who-decides-when-we-are-in-a-recession