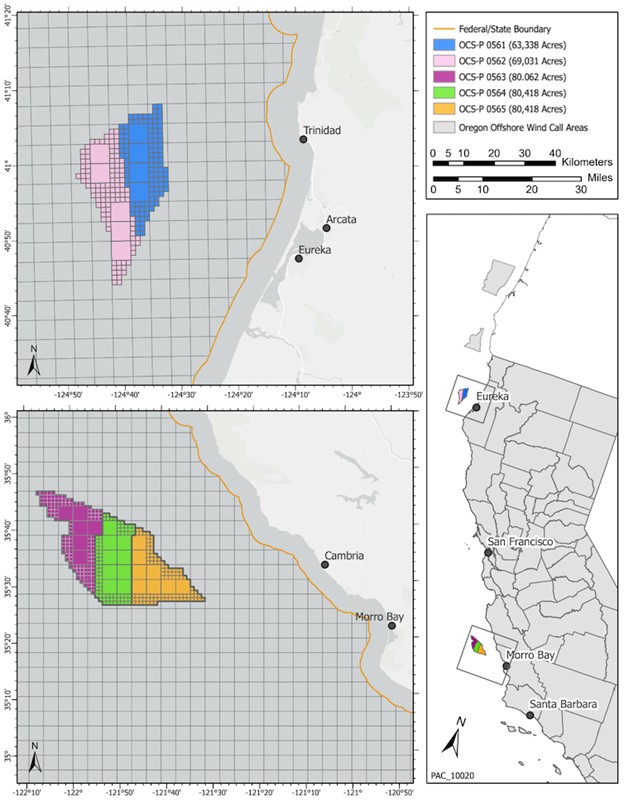
| Key Points: – Bitfarms to acquire Stronghold Digital Mining in a $175 million deal – Merger expands Bitfarms’ U.S. presence and power capacity significantly – Transaction aims to boost environmental efforts and diversify beyond Bitcoin mining |
Bitfarms Ltd. has announced its plans to acquire Stronghold Digital Mining, Inc. in a deal valued at approximately $175 million in a strategic move that’s set to reshape the Bitcoin mining landscape. This bold acquisition, slated to close in the first quarter of 2025, marks a significant milestone in Bitfarms’ growth strategy and signals a new era for both companies in the ever-evolving cryptocurrency sector.
The all-stock transaction will see Stronghold shareholders receive 2.52 Bitfarms shares for each Stronghold share they own, representing a 71% premium based on recent trading prices. This merger is poised to create a powerhouse in the Bitcoin mining industry, combining Bitfarms’ operational expertise with Stronghold’s strategic assets and power generation capabilities.
At the heart of this acquisition is Bitfarms’ ambition to expand and rebalance its energy portfolio. The company aims to increase its presence in the United States dramatically, projecting that nearly 50% of its 950 MW energy capacity will be based in the U.S. by the end of 2025. This move aligns with Bitfarms’ strategic plan to diversify geographically and tap into new power sources.
Stronghold brings to the table 4.0 EH/s of current hashrate, with the potential to scale up to approximately 10 EH/s in 2025 through fleet upgrades. The acquisition also includes two merchant power plants in Pennsylvania, providing 165 MW of nameplate generated power capacity. These facilities are recognized for their environmental benefits, converting mining waste into power and contributing to land reclamation efforts.
Perhaps most intriguing is the transaction’s potential to propel Bitfarms beyond traditional Bitcoin mining. The company sees opportunities to leverage high-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities, potentially merging these technologies with their Bitcoin mining operations. This diversification strategy could open new revenue streams and position the combined entity at the forefront of technological innovation in the crypto space.
Environmental considerations play a crucial role in this merger. Stronghold’s reclamation facilities have already rehabilitated thousands of acres of toxic waste sites, addressing historical environmental issues dating back to the 1800s. Furthermore, the potential for carbon capture projects could position Bitfarms as a leader in sustainable cryptocurrency mining practices.
The merger is expected to yield significant synergies, with an estimated $10 million in annual run-rate cost savings. This efficiency boost, coupled with the expanded power capacity and technological capabilities, positions the combined company to weather the cyclical nature of the cryptocurrency markets more effectively.
However, the road ahead is not without challenges. The transaction still requires approval from Stronghold shareholders and various regulatory bodies. Additionally, the volatile nature of cryptocurrency prices and the ever-changing regulatory landscape pose ongoing risks to the industry.
As the crypto mining sector continues to mature and face increased scrutiny over its energy consumption, this merger represents a forward-thinking approach to addressing both economic and environmental concerns. By vertically integrating power generation, expanding into strategic locations, and focusing on sustainable practices, Bitfarms is positioning itself as a leader in the next generation of cryptocurrency mining operations.
In conclusion, the Bitfarms-Stronghold merger is more than just a consolidation of assets; it’s a strategic bet on the future of Bitcoin mining and digital asset infrastructure. As the industry evolves, this union could serve as a blueprint for how cryptocurrency companies can adapt, grow, and contribute positively to both technological advancement and environmental stewardship.