Any Rail Strike Would Surely Cause Transitory Inflation
There is something I taught myself years ago as a young trader on Wall Street. I appreciate this “skill” less and less as the years go on, but it has served me well. When news breaks, my mind shifts to asking, “for what sectors is this bullish and for what sectors is this bearish?” No attachment except money movement. There will be time for personal involvement with the event after the market closes. The news of a train strike that may begin on Friday is a good example. My investor mind was quick to try and determine what companies would benefit and also which could be hurt. I have no control over whether or not it happens, but I may be able to add to portfolio returns from it. Meanwhile, at home, I’m stocking up on a few of the items often shipped by rail.
Below is some helpful information about this segment of the freight and shipping industry.
Background
Rail workers may go out on strike as early as Friday, September 16.
In the U.S. the Rail network runs almost 140,000 miles. Freight rail is an $80-billion industry operated by seven Class I railroads (railroads with operating revenues of $490 million or more), and 22 regional and 584 local/short line railroads.
More than 167,000 are employed across the U.S. It’s a safer and often more efficient means of shipping as it uses less energy and rides on a more cost-effective and safer infrastructure than trucking.
Heavy freight such as coal, lumber, metals, and liquids going long distances are likely to travel by rail or some combination of truck, rail, water, or pipeline. The rail network accounts for approximately 28% percent of U.S. freight movement by ton-miles (the distance and weight freight travels). So, by weight, 28% of what is shipped within the U.S. may get stalled in the event of a strike. This would significantly add to any supply chain issues currently being experienced.
Unlike roadways, U.S. freight railroads are owned by private organizations that are responsible for their own maintenance and improvements.
What Would be Impacted
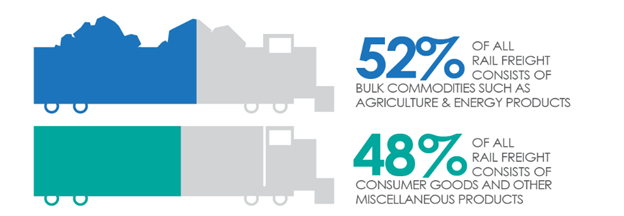
In all, 52 percent of rail freight cars carry bulk commodities such as agriculture and energy products, automobiles and components, construction materials, chemicals, equipment, food, metals, minerals, paper, and pulp. The remaining 48 percent onboard is generally being shipped in packaging that allows it to easily be moved onboard a plane, van, or other non-bulk carrier.
A rail strike would stop a high percentage of the transportation of food, lumber, coal, oil and other goods across the U.S.
Current Status
Rail stocks like Union Pacific ($UNP) and CSX ($CSX) are underperforming the market this week as rail workers’ unions continue to negotiate for higher pay and benefits. The unionized workers have the legal go-ahead to strike at the end of the week if no agreement is reached. This could impact all major U.S. railroads and cripple the supply chain on many raw materials until the dispute is settled. An immediate but temporary impact would be material shortages that would push prices up, largely at the producer level. These shortages should be resolved when the strike ends as increased price pressures should come back down. But the short-lived inflation will be additive to final goods prices for a period of time.
Eight of 12 labor unions have reached tentative agreements with railroad carriers. However, there are still disagreements over vacation, sick days, and attendance policies.
A “cooling off” period expires Friday, at which time workers can strike.
A freight rail shutdown would be expected to cost the U.S. economy around $2 billion per day, according to the Association of American Railroads. It would especially hit the energy sector hard as rail is the number one mode of transportation used by coal producers, according to the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
Take Away
A rail strike would hit multiple sectors as it could stop the transportation of food, lumber, coal, and other goods across the country. Much of what is shipped by train can’t easily be shipped by the already overburdened trucking industry.
A strike, if any, would put upward pressure on lumber, energy, and food prices. Assuming the strike gets resolved, these transit-related higher price pressures should prove to be transitory. As individuals, whether or not there is a strike is beyond our ability to change. If there is an industry sector or company that stands to improve earnings or a sector that may suffer losses, there should be no investor guilt in positioning investments in a way where the investor may prosper.
Managing Editor, Channelchek
Sources
https://railroads.dot.gov/rail-network-development/freight-rail-overview#:
https://www.barrons.com/articles/railroad-strike-truck-stocks-51663161990
