INTERNET AND DIGITAL MEDIA COMMENTARY
Internet & Digital Media Stocks Outperform – But Don’t Get Too Excited
After increasing by 8% in the second quarter of 2023, the S&P 500 was unable to hold onto those gains in the third quarter. The S&P index decreased by 4% in the third quarter, a decline which we attribute to the market revising its interest rate expectations to one in which rates would remain “higher for longer”. Large cap stocks that weighed on the broad market index included tech stocks such as Apple (AAPL: -12%), Microsoft (MSFT: -7%) and Tesla (TSLA: -4%). Despite this small step backwards, the S&P 500 Index increased by 20% through the first nine months of the year.
Each of Noble’s Internet and Digital Media Indices, which are market cap weighted, outperformed the S&P 500 in the third quarter, but the double-digit gains from the previous quarter (2Q 2023) moderated significantly. Sectors that outperformed the S&P 500’s 4% increase include Noble’s Digital Media Index (+6%), Social Media Index (+4%), Gaming Index (+3%), Ad Tech Index (+1%) and MarTech Index (-3%). Despite these relatively positive results, the prevailing theme within each sector was that the largest cap stocks performed the best while smaller cap stocks across a variety of sectors struggled.
STOCK MARKET PERFORMANCE: INTERNET AND DIGITAL MEDIA
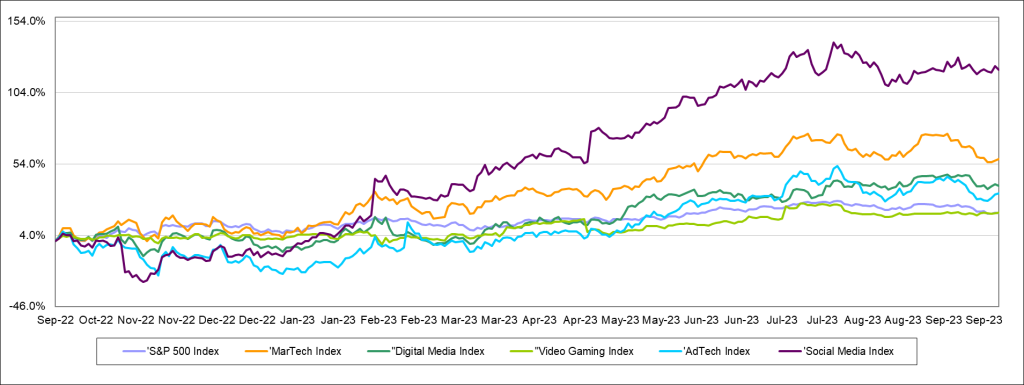
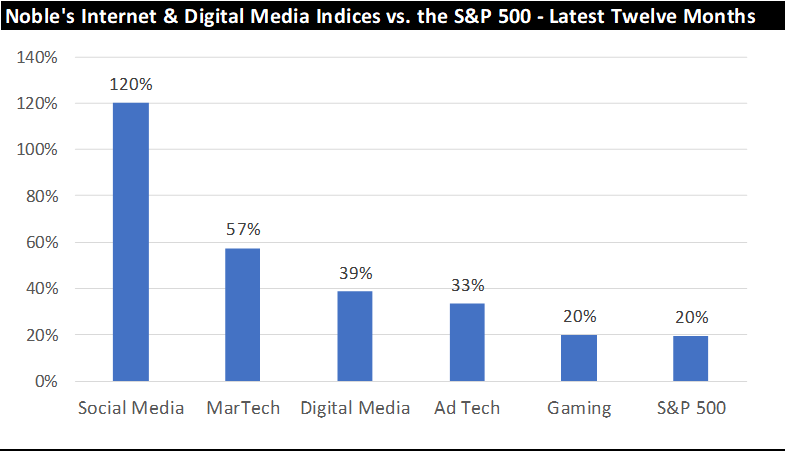
Perhaps more importantly, each of Noble’s Internet and Digital Media Indices have outperformed the S&P 500 over the latest twelve months. The S&P 500 Index has increased by 20% over the last year (through 9/30/2023), which trailed the performance of the each of Noble’s Internet and Digital Media Indices, as shown below:
Alphabet Powers Digital Media Index Higher Despite Broader-Based Sector Weakness
The best performing index during the quarter was the Noble’s Digital Media Index, but the sector’s “strong” performance is deceiving. Shares of Alphabet (a.k.a. Google: GOOGL) increased by 9% during the quarter, and the company size relative to its peers helps explain the vast majority of the sector’s performance. Google’s market cap is 8x larger than its next largest “peer” in Netflix, and it is 160 times that of the average market cap of its Digital Media peers. Google beat expectations across all metrics (revenue, EBITDA, free cash flow) and guided to improved profitability as it streamlines workflows. The company is also increasingly perceived as a beneficiary of AI. While Alphabet shares performed well, they mask the fact that shares of only 2 of the sector’s 12 stocks were up during the third quarter. The other Digital Media stock that performed well in the quarter was FUBO (FUBO), whose shares increased by 29% in 3Q 2023. Of the 10 other digital content providers in the sector, 7 of them posted double-digit stock price declines in the third quarter.
Large Cap Meta Powers the Social Media Index Higher
Shares in Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook) rose for the third straight quarter. Shares increased by 5% and were up 150% through the first nine months of the year. Meta shares increased by 8% at the start of the third quarter due to excitement around the launch of Threads, Meta’s answer to Twitter. Over 100 million people signed up for Threads within the first five days of its rollout and positions the company well for continued revenue growth once it begins to monetize this new opportunity.
As with the Digital Media Index, the in the Social Media Index masked underlying weakness across several smaller cap stocks. Of the 6 stocks in the Social Media Index, only Meta shares increased during the quarter. Several social media companies performed poorly during the quarter including Spark Networks (LOVL.Y: -59%), which filed to delist its shares, Nextdoor Holdings (KIND: -44%), which has struggled to reach profitability, and Snap (SNAP: -25%), which guided to revenue declines in 3Q 2023.
Video Gaming, Ad Tech and MarTech Indices Continue the Trend: “No Love” For Small Cap Stocks
As was the case in the Digital Media and Social Media sectors, the same trends held true in the other sectors: in general, large cap stocks outperformed small cap stocks. For example, Noble’s Video Gaming Index increased by 3% in the third quarter, driven by Activision Blizzard (ATVI: +11%), and to a lesser extent SciPlay Corp (SCP: +16%). However, 7 other stocks in the video gaming sector posted stock price declines in the third quarter. Larger cap names such as EA Sports (EA: -7%) and Take-Two Interactive (TTWO: -5%) posted mid-single digit stock price declines while every small cap video gaming stock posted double digit declines.
Noble’s Ad Tech Index increased by 1% during the quarter driven by shares of AppLovin (APP: +55%), and Taboola (TBLA: +22%). However, just 7 of the sector’s 20 stocks were up for the quarter, and 10 stocks in the sector posted double digit declines.
Finally, Noble’s MarTech Index decreased by 3% (the only index that declined during the quarter), with the sector’s largest companies, Adobe (ADBE: +4%) and Shopify (SHOP: -16%) posting mixed results. Outside of these mega-cap stocks, the theme of underlying weakness prevailed: only 5 of the 20 stocks in the sector posted stock price increases, while one was flat and the other 14 were down. Eleven of the 20 stocks in the MarTech sector posted double digit stock price declines.
3Q 2023 Internet and Digital Media M&A – A Significant Slowdown
According to Dealogic, which tracks global M&A, deal activity in North America decreased by 37% to 8,600 deals in the third quarter, however, the value of deals in North America increased by 34% to $375 billion. Dealogic noted that there was an increase in the number of scaled transactions (those with deal values in the $1 billion to $2 billion range), which increased to the highest level in 7 quarters. We did not see this phenomenon in Noble’s Internet & Digital Media sectors.
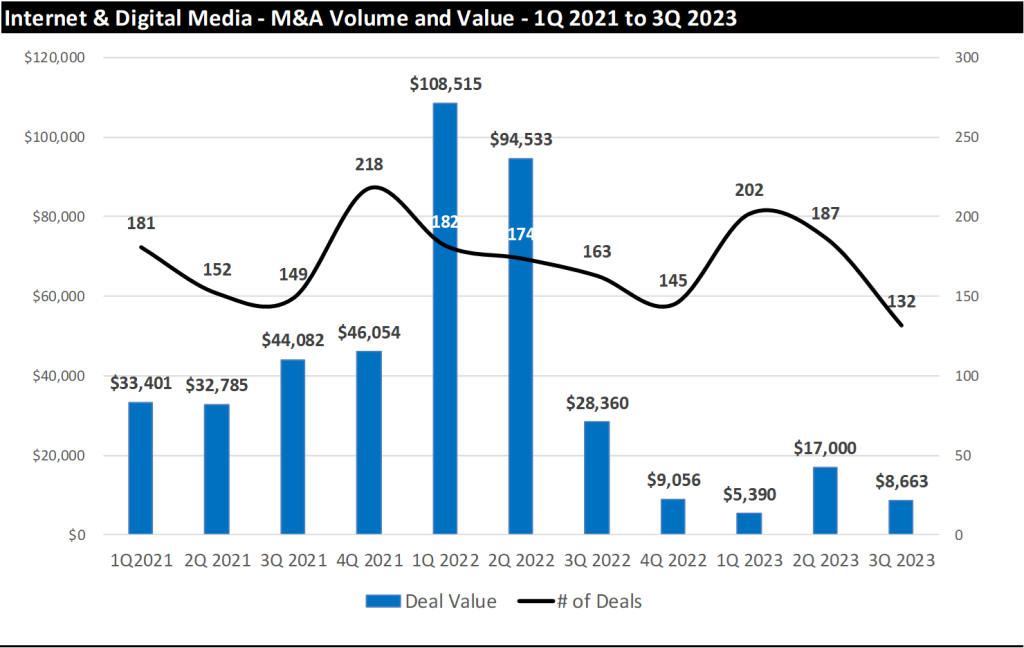
Based on our analysis, deal making in the Internet & Digital Media sectors in the third quarter of 2023 slowed rather dramatically. The total number of Internet & Digital Media deals we tracked in the quarter decreased by 29% sequentially to 132 deals in 3Q 2023 down from 169 deals in 2Q 2023. On a year-over-year basis, the total number of deals decreased by 22% to 132 deals in 3Q 2023 from 187 deals in the third 3Q 2022.
The decline in the number of deals was exceeded only by the decline in the dollar value of M&A deals. Announced M&A deal value fell sequentially by 50% to $8.7 billion in 3Q 2023 compared to $17.2 billion in announced deals in 2Q 2023. While total deal value of announced deals decreased significantly on a quarter-over-quarter basis, the decrease was even more pronounced on a year-over-year basis, as deal values decreased by 71% to $8.7 billion in deal value from $29.4 billion in 3Q 2022, as shown in the chart on the next page.
From a deal activity perspective, the most active sectors we tracked were Digital Content (39 deals), MarTech (36 deals) and Agency & Analytics (27 deals). From a dollar value perspective, Information Services led with $7.5 billion, followed by Digital Content with $633 million and MarTech with $255 million, as shown below (left).
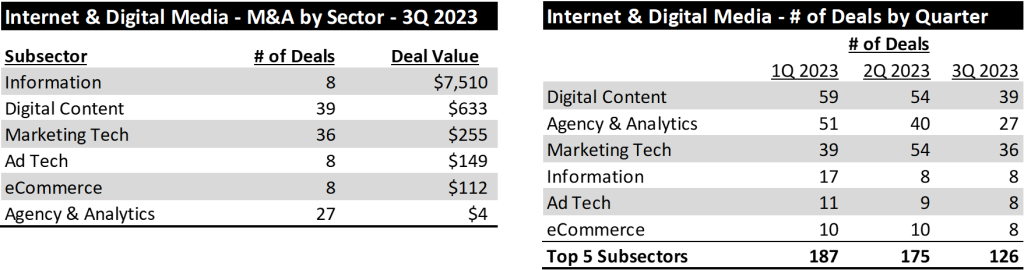
As shown above (right), the number of transactions has fallen in each of the last two quarters. Across the top 5 subsectors of Internet and Digital Media, the number of transactions has fallen from 187 transactions in the first quarter to 126 transactions in the third quarter.
We attribute this decline to a variety of factors. First, an increase in interest rates has resulted in far fewer transactions in excess of $10 billion. With rates 300 basis points higher than at the start of the year, an incremental $10 billion in debt implies a $30 million per year increase in interest expense. These higher rates result in lower returns for acquirers. Second, we believe traditional lenders have become more cautious in providing the necessary capital to fund acquisitions. Some have pointed to commercial banks and their large exposure to commercial real estate as a reason for this more cautious view. Finally, for advertising-based businesses, there are some indications that brands are waiting longer before committing to or booking ad campaigns, which has reduced visibility and made financial forecasting more difficult.
Information and Video Gaming Deals Drive the Largest Transactions in 3Q 2023
There were far fewer $100M+ transactions 3Q 2023. In the second quarter of 2023 there were 16 transactions in the Internet & Digital Media sector with transaction values greater than $100 million. In the third quarter, that amount slowed to less than half: just 7 transactions exceeded $100 million in purchase price. The Information Services sector accounted for the two largest transactions in the quarter, followed by Digital Content deals, in particular gaming deals. The list of M&A transactions that exceeded $100 million are shown in the chart below.
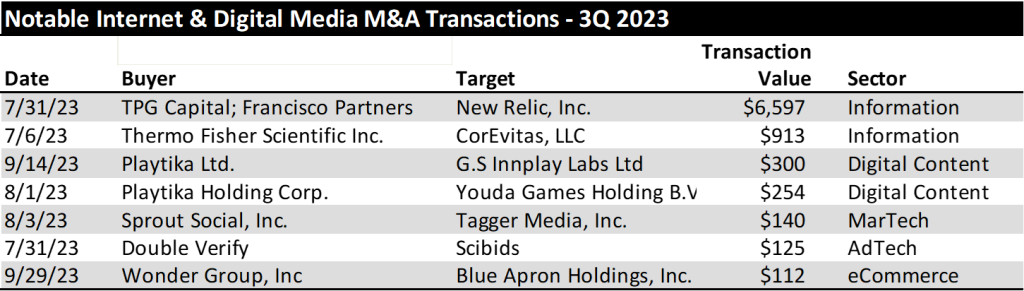
We believe the M&A market has slowed as corporations get accustomed to the prospect of higher rates for longer. One key driver of future M&A could come from distressed M&A dealmaking. Finally, another area of increased activity could come from U.S. corporations acquiring European companies where relatively weaker European currencies are making the valuations of European companies look more attractive.
TRADITIONAL MEDIA COMMENTARY
The following is an excerpt from a recent note by Noble’s Media Equity Research Analyst Michael Kupinski
Overview – The Case for Small Caps
Small cap investors have gone through a rough period. For the past several years, investors have anticipated an economic downturn. With these concerns, investors turned toward “safe haven,” large cap stocks, which typically have the ability to weather the economic headwinds and have enough trading volume should investors need to exit the position. Since 2018, small cap stocks have underperformed the general stock market, with annualized returns of just 3.7% as measured by the S&P 600 Small Cap Index versus the general market of 10.2% as measured by the S&P 500 Index. Another small cap index, the Russell 2000, increased a more modest 2.9% annually over the comparable period. The S&P 500 is larger cap, with the minimum market cap of $14.6 billion. The S&P 600 is smaller cap, a range of $850 million to $3.7 billion, with the Russell 2000 median market cap $950 million. Some of the even smaller cap stocks, those between $100 million to $850 million, have significantly underperformed the S&P 600. This is the first time that small caps underperformed a bullish period for all stocks since the 1940s. Notably, there is a sizable valuation disparity between the two classes, large and small cap, one of the largest in over 20 years.
Some of the small cap stocks we follow trade at a modest 2x Enterprise Value to EBITDA, compared with large cap valuations as high as 13x to 15x. By another measure, small cap stocks may be the only class trading below historic 25 year average to the median Enterprise Value to EBIT. Why the large valuation disparity? We believe that there is higher risk in the small cap stocks, especially given that some companies may not be cash flow positive, have capital needs, or have limited share float. But investors seem to have thrown the baby out with the bathwater. While those small cap stocks are on the more speculative end of the scale, many small cap stocks are growing revenues and cash flow, have capable balance sheets, and/or are cash flow positive. For attractive emerging growth companies, the trading activity will resolve itself over time. Some market strategists suggest that small cap stocks trade at the most undervalued in the market, as much as a 30% to 40% discount to fair value.
STOCK MARKET PERFORMANCE: TRADITIONAL MEDIA
Are we on the cusp of a small cap cycle? Some fund managers think so. Such a cycle could last 10 years or longer. In this report, we highlight a few of our small cap favorites in the Media sector, those include companies that have attractive growth characteristics, some with or without an improving economy, capable balance sheets, and limited capital needs. Our current favorites based on growth opportunity and stock valuation include: Direct Digital (DRCT), Entravision (EVC), E.W. Scripps (SSP), Gray Television (GTN), and Townsquare Media (TSQ).
Traditional Media Stock Price Performance
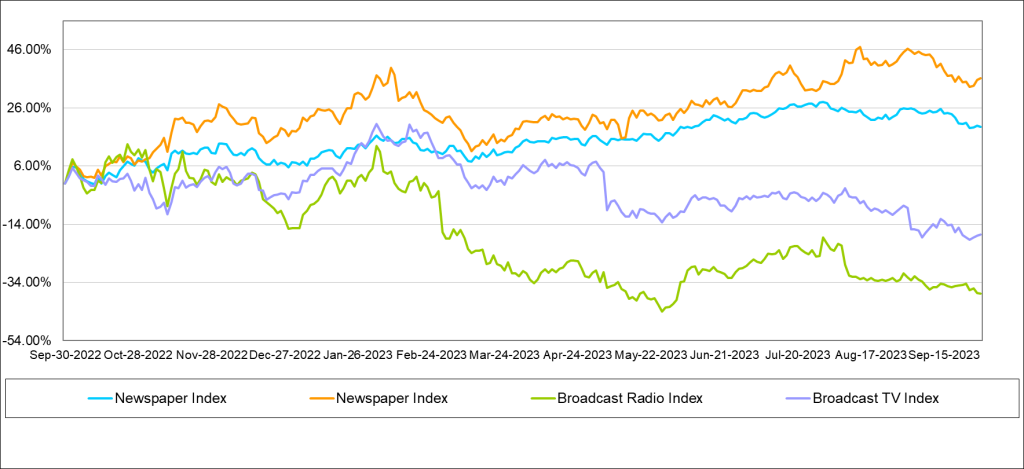
Virtually all traditional media stocks underperformed the general market in the past quarter and trailing 12 months, except for the Publishing group, as shown in the chart at the bottom of the previous page. In the latest quarter, Publishing stocks outperformed the general market, up 3% versus down 4% for the general market as measured by the S&P 500 Index. The average Publishing stock is up 7% over the past 12 months, with some of the larger cap publishing stocks up significantly more, over 20%. More details on the Publishing performance is in the Publishing section of this report. In the last quarter, the Radio stocks were the worst performing group, down on average 10%. In addition, the Radio stocks were the worst performing group in the third quarter as well, down an average of 13% for the quarter.
Broadcast Television
Have TV Stocks Been Discounted Too Much?
We believe that the economic headwinds of rising interest rates and inflation have begun to hit local advertising. Local advertising had been relatively stable, favorably influenced by a resurgence of auto advertising. Notably, local advertising fared much better than national advertising, which was down in the absence of political advertising. As we look toward the third quarter, local advertising appears to be weakening, but notably, national advertising appears to be doing much better, driven by an early influx of political advertising. While it was assumed that political would increase in the fourth quarter due to the run-off of the Republican presidential candidates, especially in early primary States, we believe that President Biden has recently stepped-up advertising, particularly to the Hispanic community. We have noticed Biden advertising even in Florida! So, what does this mean for media fundamentals?
It is difficult to predict where political dollars will be spent and not all political dollars will be spent evenly, geographically or by stations in a particular market. Furthermore, political dollars may be pulled back in a market should a particular candidate pull ahead in the polls. Political dollars were anticipated to be spent in early primary States, specifically for the Republican candidates. But the Biden money is a surprise. Biden appears to be spending early and in areas to solidify a key voting block, Hispanics. Of course, the Biden campaign may broaden its spending to other voting blocks as well. In our view, 2024 will be a banner year for political advertising given the large amount of political fundraising by the candidates and by Political Action Committees.
The prospect of weak local advertising, however, may cast a pall over the current expected strong revenue growth in 2024. Many analysts, including myself, expected that economic prospects would improve in 2024, which would have provided a favorable tailwind for a significant improvement in total TV advertising in 2024. Certainly, it is likely that the Fed may lower interest rates in 2024, potentially providing a boost to local advertising prospects, but that improvement may come late in the year. Overall, in spite of the weakening Local advertising environment, given the improving National advertising trends, overall TV advertising appears to have stabilized.
For now, we are cautiously optimistic about 2024, with the caveat that revenue growth may be somewhat tempered given the current weak local advertising trends. Nonetheless, we believe that we are nearing the trough for this economic cycle. Some companies, like E.W. Scripps, are in a favorable cycle for retransmission renewals. Retransmission revenues now account for a hefty 50% of Scripps’ total broadcast revenue. In Scripps’ case, 75% of its subscribers are under renewal, which it recently announced was completed. As such, the company reaffirmed guidance that retransmission revenue will increase 15% in 2024 and lead to a substantial increase in net retransmission revenue. We remain constructive on TV stocks, as high margin political advertising should boost balance sheets and improve stock valuations.
In the latest quarter, TV stocks underperformed the general market. The Noble TV Index decreased 13%, underperforming the 4% decline in the general market as measured by the S&P 500. The poor performance of the latest quarter adversely affected the trailing 12 month performance, bringing the Noble TV Index to a 18% decline for the trailing 12 months. Individual stocks performed more poorly, with only the shares of Fox Corporation registering a modest gain for the trailing 12 months of 3%. The Noble TV Index is market cap weighted, and, as such, Fox with a $15 billion market cap, carried the index. Outside of the relatively strong performance of this large cap stock, all of the TV stocks were down and down big, between 18% to 59% over the past 12 months.
We believe that investors have shied away from cyclicals, smaller cap stocks, and from companies with higher debt levels. This accounts for the poor performance of Gray Television (GTN) and E.W. Scripps (SSP), both of which have elevated debt leverage given recent acquisitions. Both were among the poorest performers for the latest quarter and for the trailing 12 months. GTN shares were down 12% in the third quarter and 38% for the last 12 months; the SSP shares down 40% and 58%, respectively.
We believe that the sell-off has been overdone, especially as the industry is expected to cycle toward an improved fundamental environment in 2024. As shown in the comp sheet on page 20, Broadcast TV stocks trade at a modest 5.3x Enterprise Value to our 2024 adj. EBITDA estimates, well below historic 20-year average trading multiples of 8x to 12x. We believe that the depressed valuations largely discount the prospect of an economic downturn and do not reflect the revenue and cash flow upside as we cycle into a political year. Given the steep valuation discount to historic levels, we believe that the stocks are 15% to 20% below levels where the stocks normally would be given a favorable political cycle. Our favorites in the TV space include: Entravision (EVC), one of the beneficiaries of the influx of political advertising to Hispanics; E.W. Scripps (SSP), a play on political, with the favorable fundamental tailwind of strong retransmission revenue growth; and, Gray Television (GTN), one of the leading political advertising plays.
Broadcast Radio
Shoring Up Balance Sheets
The Radio industry has struggled in the first half as National advertising weakened throughout the year. On average National advertising was down roughly 20% or more for many Radio broadcasters. Local held up relatively well, although down in the range of 3% to 5%. Fortunately, for many broadcasters, a push into digital, which grew in the first half, helped to stabilize total company revenues. As we look to the third and fourth quarters, we believe that Local advertising is weakening, expected to be down in the range of 5% to 7%, or more in some of the larger markets. For some, National advertising is improving, driven by political advertising. However, political is not evenly spread, so we anticipate that there will be a cautious outlook for many in the industry for the second half of the year.
For some in the industry, the challenged revenue environment has put a strain on managing cash flows to maintain hefty debt loads. We believe that debt leverage is among the top concerns for investors. Many of the poorest performing stocks in the quarter and for the trailing 12 months carry some of the highest debt leverage in the industry. The Noble Radio Index decreased a significant 14% in the latest quarter compared with a 4% decline for the general market. A look at the individual stock performance tells a more disappointing story. Shares of Salem Media declined 38% in the latest quarter, bringing 12-month performance to a 44% decline. Shares of iHeart Media declined 49% for the year.
Notably, Salem Media assuaged much of its liquidity concerns with recent asset sales. Such sales will bring in roughly $30 million, allowing it to fully pay off its $22 million revolver and have some flexibility with remaining cash on its balance sheet. We do not believe that investors have fully credited the significance of the recent asset sales.
One bright spot in the group was the shares of Townsquare Media (TSQ). While TSQ shares gave back a significant 27% in the third quarter, the shares are still up 20% over the past 12 months, among one of the best performing in the industry. We believe that the company’s initiation of a substantial dividend resonated with investors.
While the industry faces fundamental headwinds given the current economic challenges, we believe that most companies have made a shift toward faster growth, digital business models. In addition, we believe that Radio will see a lift from political advertising in 2024, although not to the extent that the TV industry will see. Nonetheless, we look for an improving advertising scenario in 2024, and as a result, we are constructive on the industry. One of our current favorites leads the industry in its Digital transition, Townsquare Media. As shown in the comp sheet on page 21, TSQ shares are among the cheapest in the industry, trading at 5.1x EV to our 2024 adj. EBITDA estimate, well below the average of 7.1x for the industry.
Publishing
Further Cost Cutting Will Cut Deep
Publishers are not likely to be spared from the weakening local advertising business, but publishers have a playbook on areas to cut expenses to manage cash flows. We believe that its Digital businesses should help offset some of the anticipated revenue declines on its print legacy business. We believe that the next round will cut deep into its legacy business, through the elimination of print days. Such a move likely will indicate further pressure on print revenues but would not proportionately decrease cash flow. Some print days have very little advertising and/or advertisers may shift some spending to other print days.
While many publishers would like to have a long runway for its cash flowing print business, such possible moves would accelerate the digital transition. Notably, with just some stabilization of revenues on the print side, many publishers have the potential to show total company revenue growth given benefit from digital revenue. With the prospect of strategies that may cut print days, we believe that total revenue growth may be pushed out to 2025.
Many of the Publishing stocks were written off long ago, but surprisingly, the Publishing stocks have been among the best stock performers in the latest quarter and for the trailing 12 months. The Noble Publishing Index increased a solid 36% in the trailing 12 months, outperforming the general market (as measured by the S&P 500) of 19% in the comparable time frame.
In the third quarter, Publishing stocks increased 4%, outperforming the S&P 500, which declined 4%. All of the publishers increased, with the exception of Lee Enterprises (LEE). Lee shares increased substantially a year earlier on takeover rumors. Since then, the shares have come back down to earth, while the rest of the industry moved higher. The stronger performers in the industry, however, were the larger cap companies, such as News Corp (NWSA) and The New York Times (NYT). In the latest quarter, the shares of The New York Times increased roughly 5% and the shares are up 27% for the trailing 12 months. The shares of Gannett increased a solid 9% in the latest quarter, as well.
As the Newspaper comp sheet on page 22 illustrates, there is a disparity among some of the larger, more diversified companies, like The New York Times and News Corporation. NYT shares trade at a hefty 15.7x EV to 2024 adj. EBITDA estimates, well above much of the pack currently trading in the 5x multiple range. We believe that this valuation gap should narrow, especially as many of the companies, like Lee and Gannett, have a burgeoning Digital business. While the industry faces secular challenges of its print business and there are economic headwinds in the very near term, we believe that companies like Lee Enterprises have the ability to manage cash flows and grow its digital businesses. Given the compelling stock valuation disparity, the shares of Lee Enterprises lead our list of favorites in the sector.
DOWNLOAD THE FULL REPORT (PDF)
View the PDF version for segment analysis, M&A activity, and more…
Noble Capital Markets Media Newsletter Q3 2023

This newsletter was prepared and provided by Noble Capital Markets, Inc. For any questions and/or requests regarding this news letter, please contact Chris Ensley
DISCLAIMER
All statements or opinions contained herein that include the words “ we”,“ or “ are solely the responsibility of NOBLE Capital Markets, Inc and do not necessarily reflect statements or opinions expressed by any person or party affiliated with companies mentioned in this report Any opinions expressed herein are subject to change without notice All information provided herein is based on public and non public information believed to be accurate and reliable, but is not necessarily complete and cannot be guaranteed No judgment is hereby expressed or should be implied as to the suitability of any security described herein for any specific investor or any specific investment portfolio The decision to undertake any investment regarding the security mentioned herein should be made by each reader of this publication based on their own appraisal of the implications and risks of such decision This publication is intended for information purposes only and shall not constitute an offer to buy/ sell or the solicitation of an offer to buy/sell any security mentioned in this report, nor shall there be any sale of the security herein in any state or domicile in which said offer, solicitation or sale would be unlawful prior to registration or qualification under the securities laws of any such state or domicile This publication and all information, comments, statements or opinions contained or expressed herein are applicable only as of the date of this publication and subject to change without prior notice Past performance is not indicative of future results.
Please refer to the above PDF for a complete list of disclaimers pertaining to this newsletter.



































































































