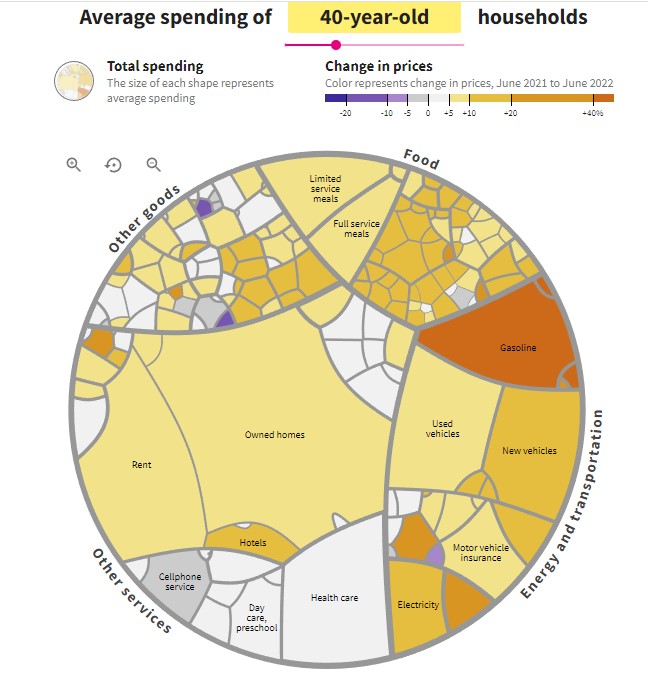
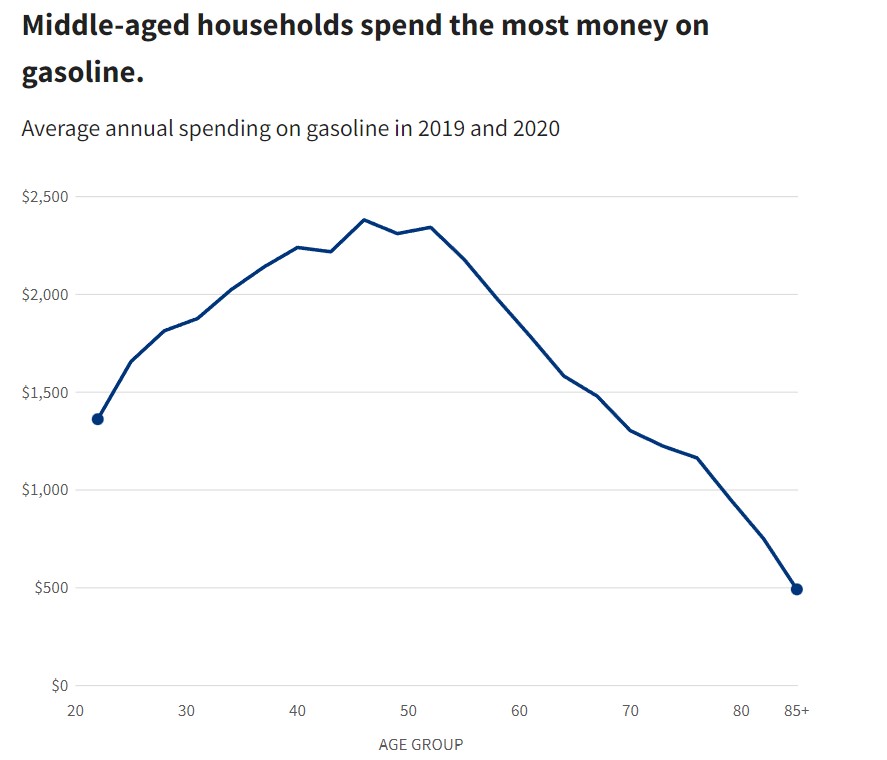
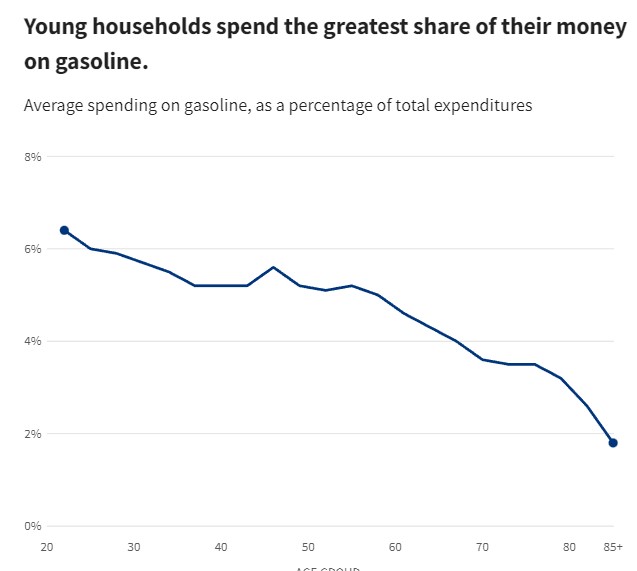
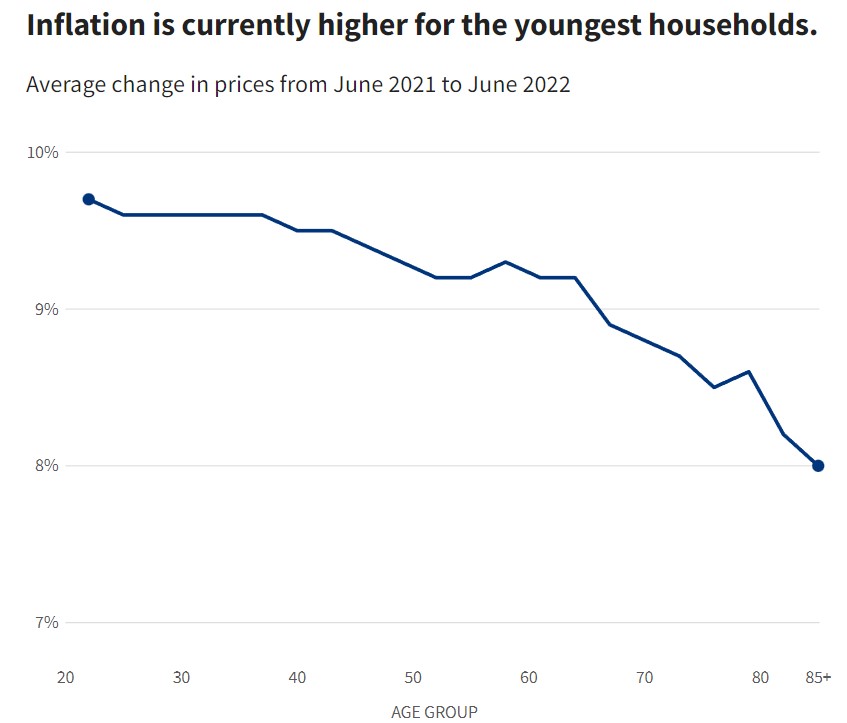
Investors Watching for a Bounce in January
Have you become accustomed to a four-day workweek? Fortunately, we all will be slowly weened off of four days on and three days off. Next week (beginning January 8) is a full five-day trading week; then, we get another three-day weekend for MLK Jr. Day (January 16). This is followed by four weeks until President’s Day, which is a national holiday. So we should all acclimate to reality without shocking the system too much.
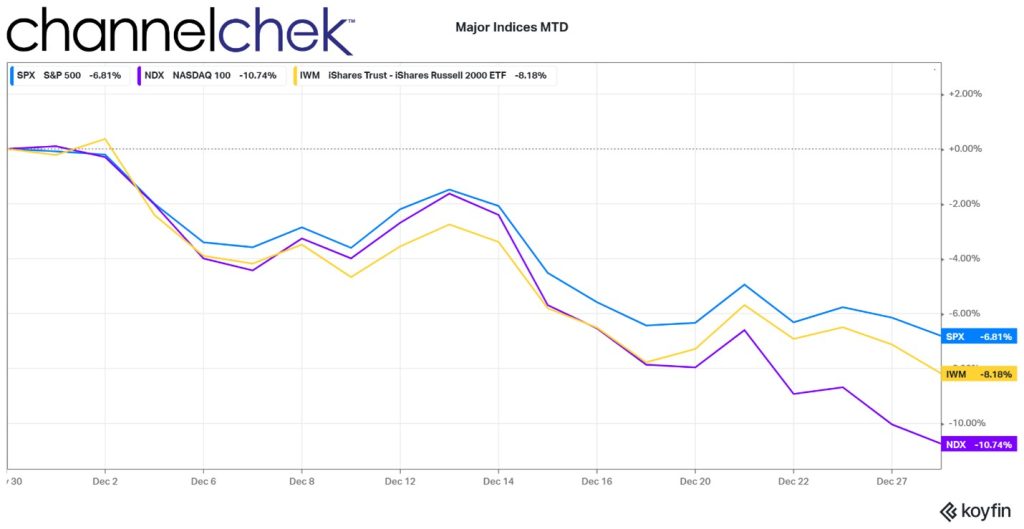
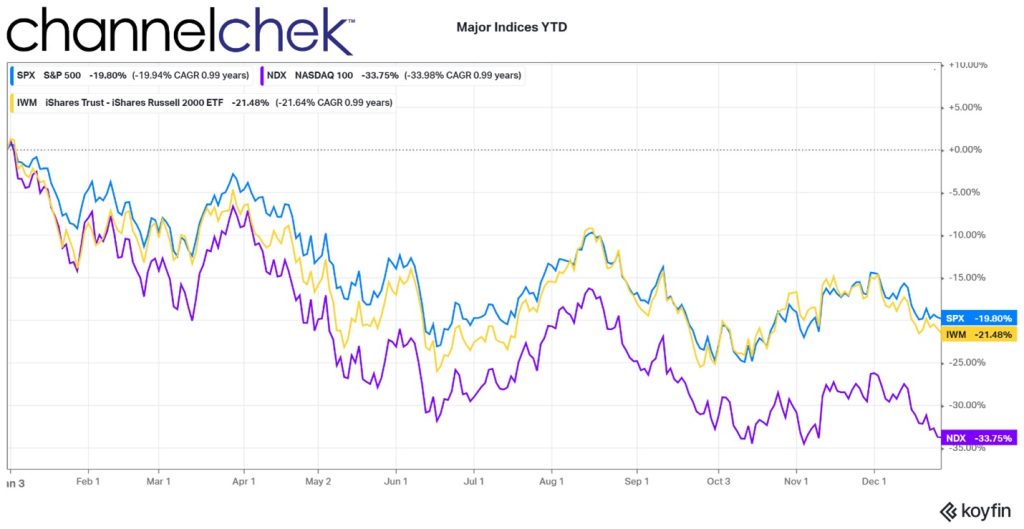
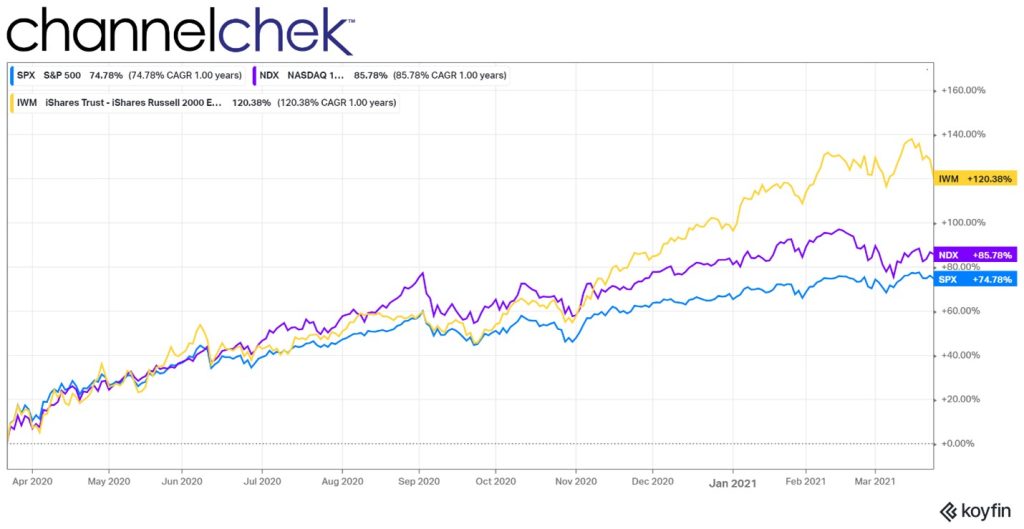
Stocks are far cheaper than they were at the start of last year. The current P/E ratio of the S&P 500 is 18.59. A year ago, that stat stood at 29.33. The last time a year ended with P/Es this low was December 2018.
A popular new year stock market axiom is the January Effect. This suggests there is a tendency for stock prices to rise in the first month of the year following a year-end sell-off. With some light number crunching, it would seem there has actually been a slight upward bias in January, but it is barely higher than that of a coin toss. Market conditions and fundamentals are probably a better focus for traders and investors. On Wednesday, the FOMC minutes for the December FOMC will be released. This may have more impact on the market’s tone to begin the new year than any market axiom.
Monday 1/2
- Markets and Government Offices closed.
- The Kuna is out as Croatia’s currency, and the Euro is in. Croatia, which has been an EU member since 2013, becomes part of the eurozone to start 2023. The integration provides open borders within the Schengen visa-free zone and the adoption of the Euro as its national currency.
Tuesday 1/3
- Treasuries that would have settled on the 31st, settle on this first business day since month end.
- 9:45 AM, PMI Manufacturing Index for December is expected to come in unchanged from the mid-month report at 46.2. This reading would indicate a contraction in manufacturing.
- 10:00 AM, Construction Spending is expected to report another weak number. After slipping 0.3 percent in October, construction spending in November is expected to fall 0.4 percent as residential building remains weak.
Wednesday 1/4
- 10:00 AM, the JOLTS report, an indicator of job openings, has shown declines since August. It is expected to show a reduction again to 10.1 million in November versus 10.3 million in October.
- 10:00 AM, the ISM Manufacturing Index is likely to confirm slowing in the sector. After gradually decelerating through the year and then entering a sub-50 contraction in November at 49.0, the ISM manufacturing index for December is expected to print at 48.0, and show a worsening decline.
- 2:00 PM, Federal Open Market Committee minutes for December. We know how this story ended; they pushed overnight rates up by 0.50%. But, the details of the issues, debates, and how much consensus there was among FOMC members three weeks later lends insight into whether the hawkish stance is fading or likely to increase. The minutes are a possible market mood changer as investors and fed watchers measure each word. The minutes will include the complete economic analysis compiled by Fed officials and opinions at odds with the consensus.
Thursday 1/5
- 7:30 AM, The Challenger Job-Cut Report is not widely followed as it includes much of the same measures as the weekly Jobless Claims. It counts and categorizes announcements of corporate layoffs based on mass layoff data from state departments of labor. Unlike most economic data, this series is not adjusted for seasonal variations; holiday layoffs could create big changes in the reading. The prior level for November was 76.84.
- 8:30 AM, Jobless Claims for the week ended December 31st are expected to creep up to 228,000 versus 225,000 the prior week. Any large variation from this expectation could be market moving as the fed closely watches the employment situation.
- 9:20 AM, the President of the Atlanta Fed, Raphael Bostic, will be speaking. Any time a voting member of the FOMC is speaking publicly, there is the possibility of insight into how that member may have recently changed their leaning on policy. Atlanta Fed events are often broadcast live on this YouTube channel.
- 4:30 PM, Fed’s Balance Sheet. This report has, in recent months, garnered more attention. This is because the weekly report of the Fed’s balance sheet provides details as to whether the pace of reductions ($95 billion monthly) is being adhered to. This represents the other tightening (QT) outlined in the current monetary policy. They are securities (treasuries and mortgaged-backed securities) that are maturing off the Fed’s balance sheet and not being replaced. This real money comes out of the economy and represents fewer dollars to hold longer-term interest rates down.
Friday 1/6
- 8:30 AM, the Employment Situation is a very closely watched economic indicator. It provides measures that both include and exclude government workers. The expected 200,000 rise for nonfarm payroll growth in December is well below the 263,000 reported in November. For each of the last seven months, this report has exceeded the consensus of economists’ projections.
- 10:00 AM, Factory Orders are a true leading indicator. They are expected to have fallen 0.6% in November.
- 11:15 AM and 3:30 PM, the President of the Atlanta Fed, Raphael Bostic, will be speaking. Any time a voting member of the FOMC is speaking publicly, there is the possibility of insight into how that member may have changed their leaning on policy. Atlanta Fed events are often broadcast live on this YouTube channel.
- 12:15 PM, the President of the Richmond Fed, Thomas Barkin, will be speaking. Any time a voting member of the FOMC is speaking publicly, there is the possibility of insight into how that member may have changed their leaning on policy.
What Else
We all have to grow accustomed to writing and typing “2023” this week. The residents of Croatia have a larger challenge, they have to convert all of their payments and transactions into euros.
The first half of the year will likely be a test of Fed Chair Jay Powell as all attention is being paid to whether monetary policy can be navigated in a way that provides for the Fed mandate of low inflation while at the same time maintaining an acceptable level of unemployment. Full employment is the Fed’s other mandate. Stock market performance usually hinges on how well the market thinks the Fed is navigating to calmer waters. December’s price action suggests room for improvement.
Managing Editor, Channelchek