
What, Why, How, Who, and When of Stock Buybacks
A certain EV Company may try to charge up its stock with a buyback.
Are stock buybacks good for companies, good for investors, and better than dividends? Last week, TESLA (TSLA) investors became excited about a tweet from founder Elon Musk that could suggest the company may bow to large shareholders and do a stock buyback. The implications for a company buying back shares and stockholders are many. Below you’ll find details on what the most typical considerations are and what it means from an investor’s standpoint.
What Is a Stock Buyback?
A stock buyback is when a public company uses cash in reserves or borrowed funds to buy shares of its own stock on the open market. A company may do this to consolidate ownership, preserve a higher stock price, boost financial ratios, work to reduce the cost of capital, or to return higher asset values to shareholders.
Investors find out when a public companies that has decided to do a stock buyback announces that the board of directors has passed a “repurchase authorization.” The amount authorized provides how much will be allocated or raised to buy back shares, or in some circumstances, the number of shares or percentage of shares outstanding it aims to purchase.
During the stock buyback, the company goes to the open market as any investor would and purchases shares of its stock in competition with other market participants. The added demand and later reduced shares available (float), puts upward pressure on the stock price. Stockholders then find their shares trade at a higher price than they would have. Shareholders are not obligated to sell their stock to the company, and a stock buyback doesn’t target any specific group of holders—retail and institutional all participate.
Public companies that have decided to do a stock buyback typically announce that the board of directors has passed a “repurchase authorization,” which details how much money will be allocated to buy back shares—or the number of shares or percentage of shares outstanding it aims to buy back.
Why Do a Stock Buyback?
The primary reason a company will buy back shares is to create value for its shareholders. Remember, fewer shares should cause those still being transacted in the open market to be trading at a higher price.
Boards of public companies’ primary responsibility are to look out for shareholders’ interests. At the top of this list is maximizing shareholder value. With this in mind, companies are always finding ways to generate the highest possible returns for their investors. This, at its most fundamental level, includes increasing the value of its stock and rewarding its investors. Buybacks and dividends work to maximize value for shareholders.
Declaring a dividend is the most direct method to return cash to shareholders; there are advantages to stock buybacks:
Tax efficiency – Dividend payments are taxed as income, whereas rising share values aren’t taxed at all. Any holders who sell their shares back to the company may recognize capital gains taxes, but shareholders who do not sell to reap the reward of a higher share value and no additional taxes until they decide when to cash in.
Directly boost share prices – The main goal of any share repurchase program is to deliver a higher share price. The board may feel that the company’s shares are undervalued, making it a good time to buy them. Meanwhile, investors may perceive a buyback as an expression of confidence by the management. After all, why would a company want to buy back stock it anticipates would decline in value?
More flexibility than dividends – Any company that initiates a new dividend or increases an existing dividend will need to continue making payments over the long term. That’s because they risk lower share values and unhappy investors if they reduce or eliminate the dividend going forward. Meanwhile, since share buybacks are one-offs, they are much more flexible tools for management.
Offset dilution – Growing companies may find themselves in a race to attract talent. If they issue stock options to retain employees, the options that are exercised over time increase the company’s total number of outstanding shares—and dilute existing shareholders. Buybacks are one way to offset this effect.
How is Value Impacted?
Key metrics investors and stock analysts use to value a public are impacted by a buyback. For example, cash is removed from a company’s balance sheet, and the number of shares trading is reduced.
Once a company has bought back its own shares, they are either canceled which reduces the number of shares available to trade (not just on the open market), or held by the company as treasury shares. These are not counted as outstanding shares, which has implications for many important measures of a company’s financial fundamentals.
Metrics important to investors, like earnings per share (EPS) are calculated by dividing a company’s profit by the number of outstanding shares. Mathematically, by reducing the number of outstanding shares, a higher EPS results as the quotient.
Price-to-earnings ratios (P/E ratio) are also mathematically improved as a higher price to the same earnings is desirable to shareholders. It helps investors measure a company’s relative valuation by comparing its stock price to its EPS.
Who Else Has Done a Buyback in 2022?
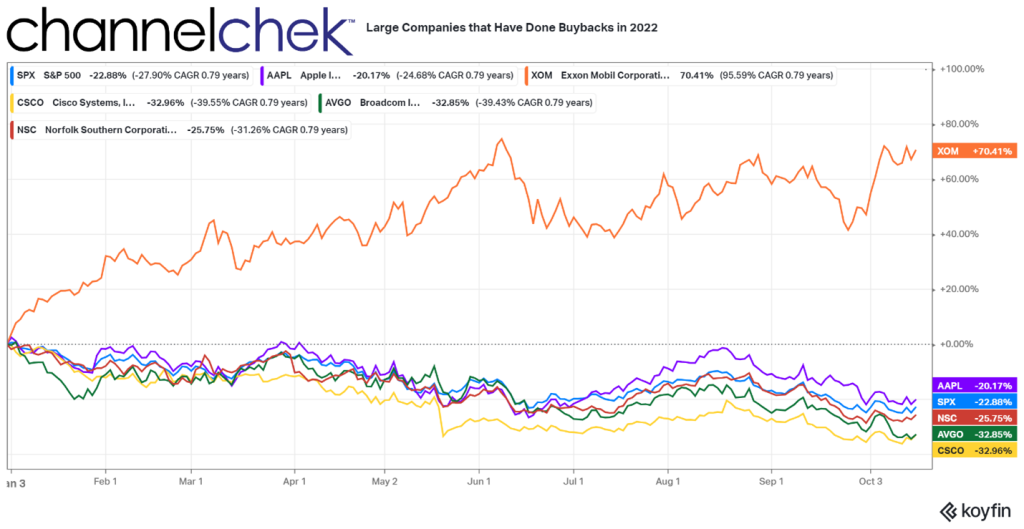
If Tesla does indeed get approval from its board of directors to buy back shares, it won’t be the only large company that has in 2022. Apple (AAPL) bought back 3.5% of its shares in May ($90 billion), Exxon (XOM) bought back 2.9% of its shares in February ($10 billion), Broadcom (AVGO) bought 4.3% of its shares in May, Cisco Systems (CSCO) bought 6.4% of its shares in February (6.4%), and Norfolk Southern purchased 14.6% of its shares ($10 billion) in March.
When Might an Investor be Against a Buyback?
In some cases, a buyback may not be the best way for companies to build value for shareholders:
It may not be the best use of cash. Long-range growth and building future profits come from investing in company growth, not company stock. Stockholders may prefer, depending on available opportunities for the company and other variables, that the company take a longer-term view. Stock buybacks create quick price gains but may not be the best long-term use of cash. Also, cash for a potential unforeseen challenge to the company could be comforting to some investors, depending on the situation.
When interest rates are low, companies increase their debt-financed share buybacks. In the years just prior to the pandemic, up to half of all buybacks were financed using the low-interest rates at the time. Below-average interest rates incentivized companies to borrow money to spend on share buybacks to boost stock prices. Depending on the scenario, this debt on the balance sheet may long-term weigh on shareholders.
Take Away
Profitable public companies may add value for investors through a stock buyback, also known as share buyback or share repurchase program.
If you are invested in Tesla or another company that may announce a share repurchase program, is this something to be happy about? As a rule, if a public company is profitable, has the cash to spare and its shares are relatively undervalued, then a buyback could be a positive, especially short term.
However, if the company is repurchasing shares of stock while it stymies future growth potential, it could cost long-term investors.
Managing Editor, Channelchek
Sources
https://www.barrons.com/articles/tesla-stock-price-buyback-51665733744?noredirect=y