
Industries are Impacted in Multiple Ways by Rising Gas Prices
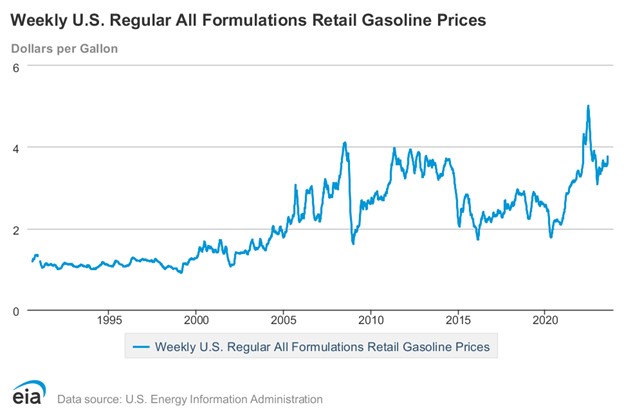
High gas prices have again become a consideration when planning a roadtrip. The rollercoaster ride of very highs, then lows, and back again to highs, since the beginning of the decade has been numbing. The uncertainty of changing costs from one season to another has made it difficult for both businesses to plan, and for any individual driver, it all impacts decisions well beyond your weekend getaway.
Over the years, the price at the pump was driven up from factors such as geopolitical tensions, storms including hurricanes, a flood in Mississippi, and normal heightened demand during the summer driving season. On an individual level, increased gasoline costs translate to less disposable income for other necessities and luxuries. But, from an investor standpoint, the ramifications of soaring gas prices reach far beyond the service station, it deeply affect the broader economy and industry segments.
Conversely, plummeting gas prices mean lighter expenditures for households and businesses alike, relieving financial strains on transport-centric sectors such as airlines and trucking. However, these price drops also cast a shadow on some industries, especially the oil sector.
Below we highlight the direct and indirect adverse repercussions of high gas prices.
The Economic Ripples of Gas Prices
Employment
Job growth serves as a pivotal indicator of an economy’s recovery, and economists warn that surging gas prices could undermine hiring practices. Gas prices might prompt businesses to rethink their hiring plans, leading to a temporary hold as uncertainty about the economy’s well-being unfolds. Decreased discretionary spending and sales can influence a company’s hiring capacity.
Retailers
An indirect effect of soaring gas prices is a reduction in consumer discretionary spending due to a larger share of income being budgeted toward gasoline. Higher prices also induce consumers to drive less, even to places like malls and shopping centers. This is substantiated by both academic and industry studies, showing a direct correlation between driving miles and gas prices.
While shoppers might cut back on driving, they tend to increase online shopping when gas prices climb. Searches for online shopping surge in tandem with escalating gas prices.
Nonetheless, all retailers face added pressure to pass on the increased expenses they incur, particularly in shipping costs to consumers. Anything requiring transportation, from lumber to electronics, could incur higher costs due to surging gas prices. This holds true for products manufactured overseas or components sourced internationally. Moreover, products containing petroleum-derived materials or plastics also experience price hikes.
Auto Industry
Historically, the automobile industry responds to surging gas prices by producing smaller, more fuel-efficient vehicles, such as hybrids and all-electric cars capable of traveling long distances on a single charge. Consumers have shown robust support for this shift, evident from the upward trajectory of hybrid and all-electric vehicle sales in the United States since 2010, while sales of gas-guzzling trucks and SUVs lag.
Airlines
Fuel expenses are the single largest operational costs for airlines, constituting a substantial proportion of their overhead. Hence, fluctuations in oil prices significantly impact their bottom line. With rising gas prices, airlines are compelled to hike ticket prices, potentially discouraging non-essential air travel and burdening consumers financially.
To hedge against volatile oil costs, airlines often engage in fuel hedging, buying or selling expected future oil prices through various investment products. This strategy safeguards airlines from surging prices and sometimes even capitalizes on them.
New Jobs and Freelancers
Prospective job candidates must factor in commuting costs when evaluating potential positions. Some workers have had to decline job offers due to the exorbitant costs of commuting, consuming a significant chunk of their salary. Freelancers, most directly Uber and Lyft drivers, also feel the impact of higher gas prices, limiting their geographical scope of business as commuting expenses render some gigs unprofitable.
Take Away
Rising gas prices usually parallel a growing pessimism about the economy. While economists and analysts may debate the precise degree to which gas prices affect the economy, there undeniably exists a connection between consumer confidence, spending behaviors, and gas prices. This mood and actual level of sales have an impact on stock market activity, depending on how long fuel prices are expected to stay high (or low).
Managing Editor, Channelchek