Fitch Has Placed the United States and Some of its Debt on Credit Watch
What does it mean that rating agency Fitch has put the US debt on credit watch?
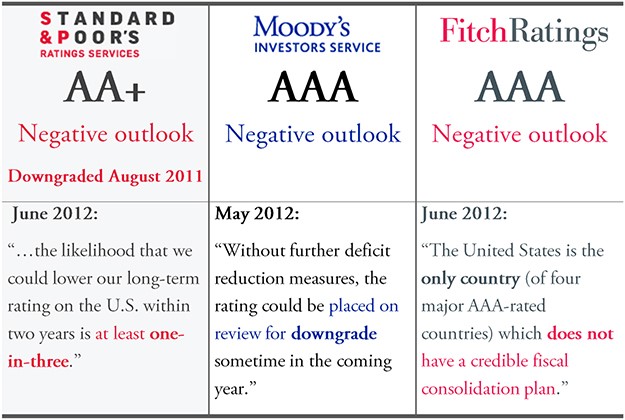
According to Fitch Ratings, a rating service that is one of the top three Nationally Recognized Statistical Rating Agencies (NRSRO), has placed the United States AAA Long-Term, Issuer Default Rating (IDR) on rating watch and at risk of a downgrade. The primary reason for the rating agency warning is the apparent standstill of negotiations related to the US borrowing limit along with the approaching day that the US may not be able to refinance the interest portion of approaching US Treasury Bills (T-Bills), US Treasury Notes (T-Notes), and US Treasury Bonds (T-Bonds).
Implications
When a top credit rating agency places a country’s debt on credit watch, it means that the agency is considering lowering that country’s credit rating if conditions remain unchanged or worsen. This would have a number of negative consequences for the country, and could negatively impact those that operate within its economy, this could include:
- Higher interest rates on government borrowing
- Higher rates on corporate debt priced off of US Treasuries
- Higher mortgage rates spread to US Treasuries
- A decline in the value of the country’s currency
- Increased difficulty in attracting foreign investment
A downgrade of the US government credit rating below AAA would be a major event with far-reaching consequences above and beyond the immediate impacts bullet-pointed above.
Wording of the Fitch Ratings Warning
Rating agencies like Fitch, Moody’s, and S&P are private companies. Debt issuers pay to have their debt issues rated to provide investors with information and a framework of value. These rating agencies or NRSROs are somewhat akin to providers of equity research to stock market participants via company-sponsored research.
Some of the main categories listed by Fitch titled, KEY RATING DRIVERS, are “Debt Ceiling Brinkmanship”, “Debt Limit Reached”, “X-Date Approaching”, “Debt Default Rating Implication”, “Potential Post Default Ratings”, and “High and Rising Public Debt Burden”.
The concern with debt ceiling brinkmanship according to Fitch is the “increased political partisanship that is hindering reaching a resolution to raise or suspend the debt limit despite the fast-approaching x-date (when the U.S. Treasury exhausts its cash position and capacity for extraordinary measures without incurring new debt).”
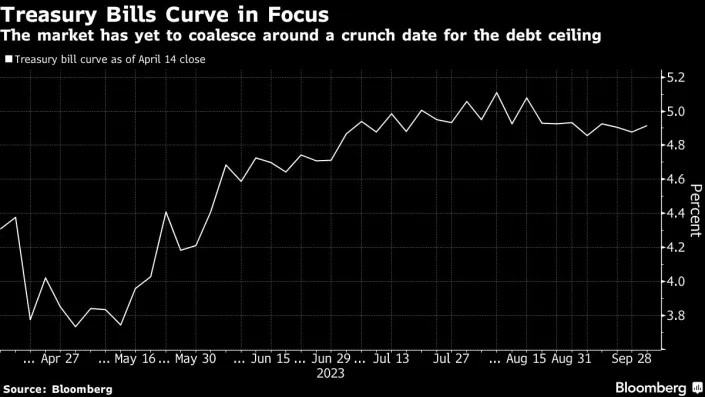
Fitch’s warning indicates it still expects a resolution to the debt limit before the x-date. However, it believes risks have risen that the debt limit will not be raised or suspended before the x-date and that the government could begin to miss payments on some of its obligations.
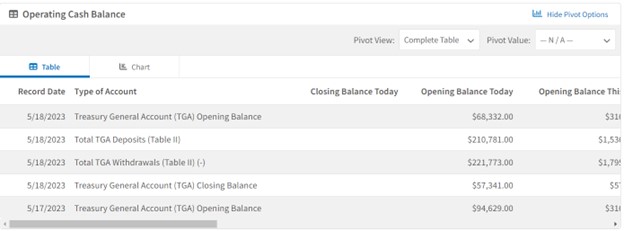
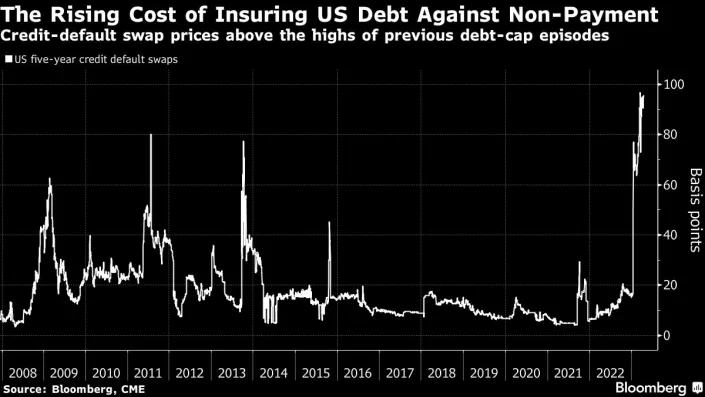
Fitch pointed out that the US reached its $31.4 trillion debt ceiling on Jan. 19, 2023. While the US Treasury has taken what Janet Yellen called “extraordinary measures” she also expects the measures could be exhausted as early as June 1, 2023. The cash balance of the Treasury reached USD76.5 billion as of May 23, and sizeable payments are due June 1-2.
The x-date has been defined as the day the US can’t meet its obligations without borrowing above the current Congressional debt limit. Failure to reach a deal “to raise or suspend the debt limit by the x-date would be a negative signal of the broader governance and willingness of the U.S. to honor its obligations in a timely fashion,” Fitch warned. The rating agency indicated this “would be unlikely to be consistent with a ‘AAA’ rating”
Fitch also addressed the 14th amendment discussions and other unconventional solutions, “avoiding default by non-conventional means such as minting a trillion-dollar coin or invoking the 14th amendment is unlikely to be consistent with a ‘AAA’ rating and could also be subject to legal challenges,” Fitch advised.
The debt default rating warning comes from basic understanding of the role of a rating agency. However, Fitch did offer an opinion on the likelihood. “We believe that failing to make full and timely payments on debt securities is less likely than reaching the x-date, and is a very low probability event.
If a default did occur, Fitch indicated it would be more than one level adjustment to some debt affected. Fitch’s sovereign rating criteria would lead it to downgrade the sovereign rating (IDR) to Restricted Default (RD). Actual affected securities would be downgraded to ‘D’. Additionally, other LT debt securities with payments due within 30 days could be expected to be downgraded to ‘CCC’, and ST T-Bills maturing within the following 30 days could be expected to be downgraded to ‘C’.
“Other debt securities with payments due beyond 30 days would likely be downgraded to the expected post-default rating of the IDR,” Fitch wrote.
The US has a high and rising public debt burden, according to the rating agency. It points out that government debt fell to 112.5% of GDP at year-end 2022 (compared to 36.1% for the ‘AAA’ median). It peaked during the pandemic at 122.3%. Fitch forecasts debt to increase to 117% by end-2024. Debt dynamics under the baseline Congressional Budget Office (CBO) assumptions project that the ratio of federal debt held by the public to GDP will approach 119% within a decade under the current policy setting, a rise of over 20 pp. Fitch also recognizes the added cost of financing, adding, “interest rates have risen significantly over the last year with the 10-year Treasury yield at close to 3.7% (compared to 2.8% a year ago).”
Take Away
The decision to put a country’s debt on credit watch is not made lightly. One company announcement such as this can have an impact felt across the globe. It’s important for them to get this right. NRSROs typically would only put a sovereign nation, especially the US, where its debt is often called “the risk free rate,” and the US dollar serves as fiat currency. Firch did this because they view it as responsible and in line with what securities analysts and the rating services they work for are expected to watch out for.
In the current case of the United States debt ratings, the main concern is the political gridlock in Washington, which has made it difficult to reach an agreement on raising the debt ceiling. If the debt ceiling is not raised, the United States will eventually run out of money to pay its bills, which would trigger a default. Fitch would be embarrassed (and arguably irresponsible) if they maintained a AAA rating just one week before the US Treasury Secretary indicated the nation couldn’t roll its debt.
Managing Editor, Channelchek
Sources