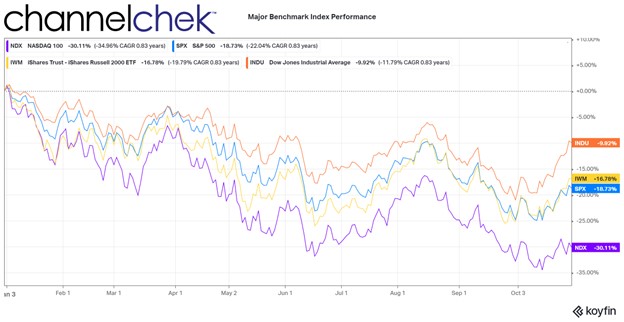
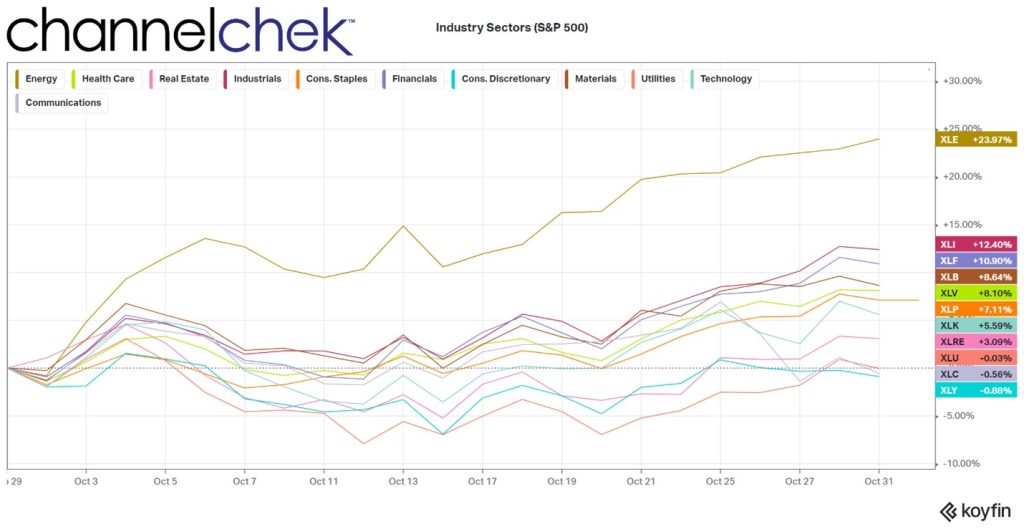
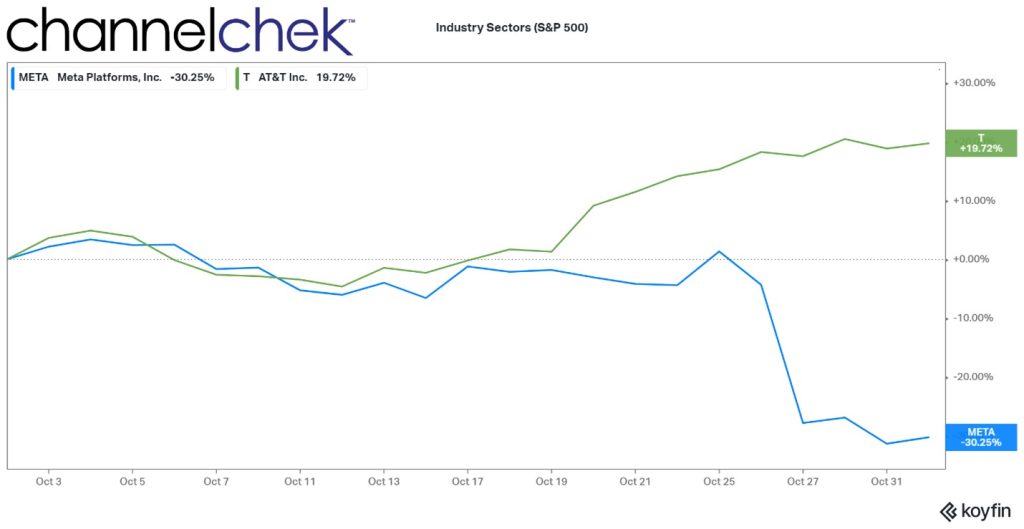
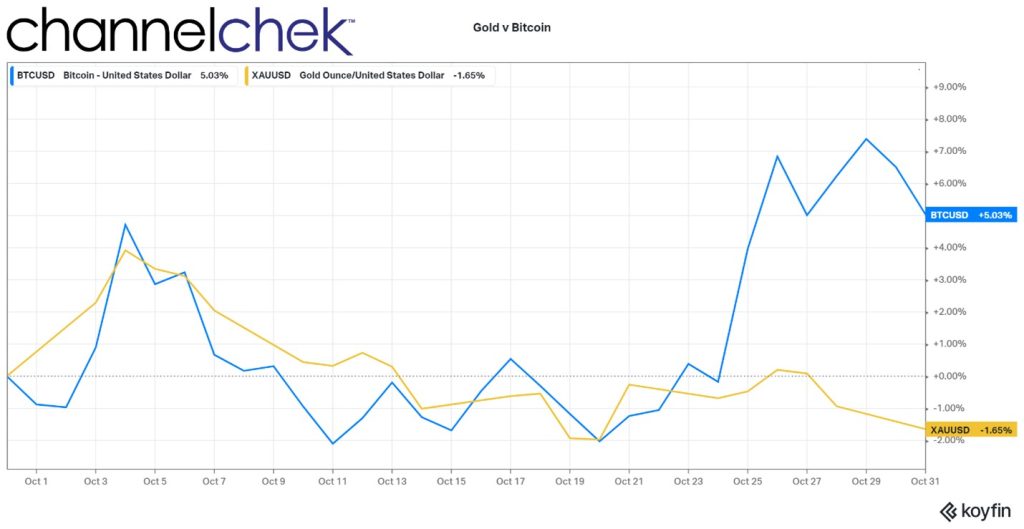
Can the Dollar Once Again Be Anchored by Gold? One Congressman Believes It Can
On October 7, 2022, US congressman Alex Mooney (a Republican from West Virginia) introduced a bill (the Gold Standard Restoration Act, H.R. 9157) that stipulates that the US dollar must be backed by physical gold owned by the US Treasury. The initiative clearly indicates that the increasingly inflationary US dollar is triggering efforts to get better money.
It should be noted that there have already been many legislative changes to make precious metals more attractive as a means of payment in recent years: in many US states, the value-added and capital gains taxes on gold and silver, but also on platinum and palladium, have been abolished. Mr. Mooney’s proposal is divided into three sections.
The first section of the bill establishes the need for a return to a gold-backed US dollar. For example, it is said that the US dollar—or more precisely, the bill refers to “Federal Reserve Notes”—that is, banknotes issued by the US Federal Reserve (Fed)—has lost its purchasing power on a massive scale in the past: Since 2000, it has dropped by 30 percent, and since 1913 by 97 percent. The bill also argues that with an inflation target of 2 percent, the Fed will not preserve the purchasing power of the US dollar but will have it halved after just thirty-five years. Moreover, the bill points out that it is in the interest of US citizens and firms to have a “stable US dollar.” The bill highlights that the inflationary US dollar has been eroding the industrial base of the US economy, enriching the owners of financial assets, while endangering workers’ jobs, wages, and savings.
The second section of the bill describes in more detail the technical process for re-anchoring the US dollar to the US official gold stock. It states that (1) the US secretary of the Treasury must define the US dollar banknotes using a fixed fine gold weight thirty days after the law goes into effect, based on the closing price of the gold on that day. The Fed must (2) ensure that the US banknotes are redeemable for physical gold at the designated rate at the Fed. (3) If the banks of the Fed system fail to comply with peoples’ exchange requests, the exchange must be made by the US Treasury, and in return, the Treasury takes the Fed’s bank assets as collateral.
The third section specifies how a “fair” gold price in US dollar can develop in an orderly manner within thirty days after the bill has taken effect. To this end, (1) the US Treasury and the Fed must publish all of their gold holdings, disclosing all purchases, sales, swaps, leases, and all other gold transactions that have taken place since the “temporary” suspension of the redeemability of the US dollar into gold on August 15, 1971, under the Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944. In addition, (2) the US Treasury and the Fed must publicly disclose all gold redemptions and transfers in the 10 years preceding the “temporary” suspension of the US dollar’s gold redemption obligation on August 15, 1971.
What to Make of This?
The bill’s core is the idea of re-anchoring the US dollar to physical gold based on a fair gold price freely determined in the market. (By the way, this is an idea put forward by the economist Ludwig von Mises (1881–1973) in the early 1950s.) In this context, the bill refers to US banknotes. However, banknotes only comprise a (fractional) part of the total US dollar money supply. But since US bank deposits can be redeemed (at least in principle) in US banknotes, not only US dollar cash (coins and notes) could be exchanged for gold, but also the money supply M1 or M2 as fixed and savings deposits could be exchanged for sight deposits, and sight deposits, in turn, could be withdrawn in cash by customers, and the banknotes could then be exchanged for gold at the Fed.
As of August 2022, the stock of US cash (“currency in circulation”) amounted to $2,276.3 billion. Assuming that the official physical gold holdings of the US Treasury amount to 261.5 million troy ounces, and the market expected US cash to be backed by the official US gold stock, a gold price of about $8,700 per troy ounce would result. This would correspond to a 418 percent increase compared to the current gold price of $1,680. If, however, the market were to expect the entire US money supply M2 to be covered by the official US gold stock, then the price of gold would move toward $83,000 per troy ounce—an increase of 4.840 percent compared to the current gold price. Needless to say, such an appreciation of gold has far-reaching consequences.
All goods prices in US dollars can be expected to rise (perhaps to the extent that the price of gold has risen). After all, the purchasing power of the owners of gold has increased significantly. Therefore, they can be expected to use their increased purchasing power to buy other goods (such as consumer goods, but also stocks, houses, etc.). If this happens, the prices of these goods in US dollar terms will be pushed up—and thus, the initial purchasing power gain that the gold dollar holders have enjoyed by being tied to the increased gold price will melt away again. Moreover, if US banks were willing to accept additional gold from the public in exchange for issuing new US dollar, reanchoring the US dollar in gold would increase the upward price effect.
A re-anchoring of the US dollar in the US official gold stock will result in a far-reaching redistribution of income and wealth. In fact, it would be fatal for the outstanding US dollar debt: US dollar goods prices would rise, caused by a rise in the US dollar gold price at which the US dollar is redeemable for physical gold, thereby eroding the US dollar’s purchasing power. In the foreign exchange markets, the US dollar would probably appreciate drastically against those currencies that are not backed by gold and against currencies which are backed by gold, not as fine compared to the fineness of the gold backing of the US dollar. The purchasing power of the US dollar abroad would increase sharply, while the US export economy would suffer. US goods would become correspondingly expensive abroad, while foreign companies gain high price competitiveness in the US market.
Once the US dollar is re-anchored in gold, today’s chronic inflation will end; monetary policy–induced boom-and-bust cycles will come to an end; the world will become more peaceful because financing a war in a gold-backed monetary system will be very expensive, and the general public will most likely not want to bear its costs. However, there is still room for improvement. A “Gold Standard Restoration Act” will deserve unconditional support if and when it paves the way toward a truly “free market for money.” A free market in money means that you and I have the freedom to choose the kind of money we believe serves our purposes best; and that people are free to offer their fellow human beings a good that they voluntarily choose to use as money.
In a truly free market, people will choose the good they want to use as money. Most importantly, in a truly free market in money, the state (as we know it today) loses its influence on money and money production altogether. In fact, the state (and the special interest groups that exploit the state) no longer determine which kind of gold (coins and bars, cast or minted) can be used as money; the state is no longer active in the minting business and cannot monopolize it anymore; there is no longer a state-controlled central bank to intervene in the credit and money markets and influence market interest rates. That said, let us hope that the Gold Standard Restoration Act proposed by Mr. Mooney will pave the way to reforming the US dollar currency system—and that it will eventually move us toward a truly free market in money.
About the Author
Dr. Thorsten Polleit is the Chief Economist of Degussa and an Honorary Professor at the University of Bayreuth. He also acts as an investment advisor.