Afghanistan Is Sitting on a Gold Mine. Literally
Afghanistan is sitting on a gold mine. I don’t mean that figuratively.
The country sits atop what could be one of the world’s largest reserves of various metals and minerals, including not just gold but also platinum, silver, copper, iron, aluminum and uranium. It’s believed to have so much lithium, an increasingly important metal that’s widely used in battery technology, that Afghanistan could one day be known as the “Saudi Arabia of lithium,” according to a 2010 memo by the U.S. Department of Defense.
The combined value of its minerals is estimated at between $1 trillion and $3 trillion. By comparison, opium poppy production in the country was valued at only $350 million in 2020, despite an increase in cultivation from the previous year.
|
This article was republished with permission from Frank Talk, a CEO Blog by Frank Holmes of U.S. Global Investors. Find more of Frank’s articles here – Originally published August 30, 2021 |
Afghanistan Rich in All-Important REEs. Will They Fall into the Right Hands?
Among Afghanistan’s rich resources are rare earth elements (REEs). REEs are those metals with unpronounceable names that are used in the manufacture of advanced technologies, including electric vehicles, wind turbines and missile guidance systems. Your iPhone contains a number of them. Each F-35 fighter jet carries about half a ton of these strategic elements.
As I’ve shared with you before, China has virtually cornered the global REE
market. The U.S. has only one developed deposit—the Mountain Pass Mine near Las Vegas, owned by MP Materials—which supplies about 15.8% of the world’s REEs. In October 2020, former President Donald Trump signed an executive order addressing America’s overreliance on these “critical minerals” from “foreign adversaries,” including China.
And speaking of China, it’s not letting a good opportunity go to waste. Mere hours after the Taliban completed its swift takeover of Afghanistan, a Chinese foreign ministry spokesperson said that Beijing was
ready to participate in
“Afghanistan’s reconstruction and development.”
I genuinely hope the development of Afghanistan’s resources, with or without China’s help, improves its citizens’ quality of life and brings the country into the 21st century. With time, and with the right execution, Afghanistan could become one of the wealthiest countries in the region.
That said, the odds are not in the country’s favor, sadly. The so-called
“resource curse” is a real thing.
REE Miners on a Tear
Due to their scarcity and increasing strategic importance in advanced technologies, from lasers to X-rays to fiber optics, prices for many rare earths are elevated and are expected to continue rising.
This has been good for producers. As measured by the MVIS Global Rare Earth/Strategic Metals Index, shares of the group are up nearly 180% for the 12-month period, compared to producers of more conventional metals, which have risen 28%.
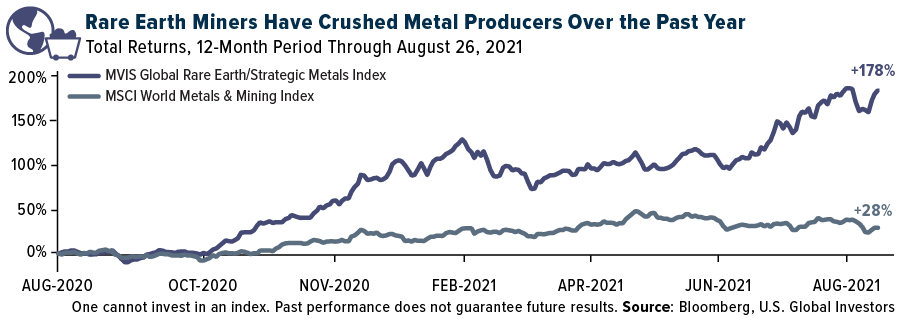
In July, in fact, the rare earth index was up a whopping 26%, making it MV Index Solutions’ top performing hard asset index for the month. The biggest mover for the month was China Northern Rare Earth High-Tech Company, up 130%, mostly on expectations of even higher demand from the electric vehicle (EV) sector, which could have a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 46% over the next five years. China’s carbon neutrality ambitions are another driver, with REEs being needed for wind turbines, solar arrays and more.
We like number two company Standard Lithium, up 47% in July. A speculative play, the Vancouver-based company, which has projects in Arkansas and San Bernardino Country, California, began trading in New York in July under the ticker SLI.
Lithium is a key component in the production of batteries, the demand for which is expected to jump many times over as the world transitions to the electrification of everything. Case in point: Last week, California announced it would increase its solar and wind power
capacity this year to help meet its target of 50% renewable energy generation by 2025. Toward that end, the state plans to add another 1.6 gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity and 0.4 GW of onshore wind capacity in 2021, along with 2.5 GW of battery storage capacity.
New Touchscreen Tech Constructive for Silver
We’re also bullish on silver for the same reasons. As Metals Focus reports last week, a growing number of countries are installing greater than 1 GW of photovoltaic (PV) capacity for solar power. In 2020, this number stood at 18, compared to 11 in 2018. Metals Focus also notes that replacement PV cells are constructive for the white metal, as “very little silver is recovered from old PV cells.”
Also adding to my bullishness is news that a new technique to make the conductive glass found in touchscreens, one using silver, may soon replace current methods that use a metal called indium.
Although indium is not technically a rare earth element, its economics are very much the same. About 70% of known deposits are in China. Output is unstable, with much of the supply existing only as a byproduct of zinc mining. And yet it’s used to make the ubiquitous touchscreens found in smartphones, laptops, ATMs, car stereos, cash registers and more.
An Australian scientist may have developed a solution that would help the world wean itself off of indium. Writing in the Conversation, Behnam Akhavan says that he and his team at the University of Sydney have discovered a way to make touchscreens with silver and tungsten oxide instead of indium. “The entire process takes only a few minutes, produces minimal waste, is cheaper than using indium, and can be used for any glass surface such as a phone screen or window,” Akhavan writes, adding that he’s conducting further research to adapt the technology for wearable electronic devices.
“The entire process takes only a few minutes, produces minimal waste, is cheaper than using indium, and can be used for any glass surface such as a phone screen or window,” Akhavan writes, adding that he’s conducting further research to adapt the technology for wearing electronic devices.
This is positive news for silver demand, which is already strong from the renewable energy industry. Last week, Russian producer Polymetal International says it sees greater industrial demand pushing the white metal up to $30 an ounce, compared to $24 today.
Investors Losing 4% on the 10-Year Treasury
The (virtual) Jackson Hole Economic Symposium was last Friday, and Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell suggested what’s been on everyone’s mind for weeks now. The central bank may begin tapering its monthly bond-buying program by the end of the year, though rates are unlikely to be hiked just yet. That’s despite inflation running above 5% year-over-year. That’s despite inflation running above 5% year-over-year.
This just means bond yields will be negative for longer, benefiting gold and precious metals. The 10-year yield fell nearly 5 basis points on Friday to 1.30%. When adjusted for inflation, investors are paying the government 4% for the pleasure of holding its debt.
Take a look at what German investors are doing in the face of potentially higher inflation. Purchases of gold bars and coins in the first half of 2021 rose to their highest levels since at least 2009.
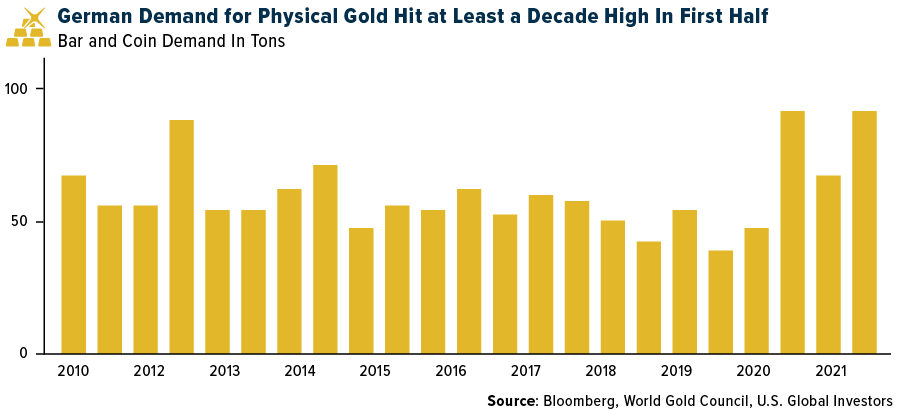
As always, I recommend a 10% weighting in gold, with 5% in physical bullion and 5% in gold mining stocks and ETFs. It’s important to rebalance on a regular basis.
-Frank Holmes, CEO U.S. Global Investors, Inc.
Channelchek invites you subscribe to the U.S. Global Investors
YouTube channel by clicking here!
Suggested Reading:
 The Taliban Assumes Stewardship of Afghanistan’s Rich Strategic Mineral Resources
|
 High Tech Search for Copper
|
 Holiday Gift-Giving Season May Include More Gift Cards and IOUs
|
 What Metals Prices Can Tell Us About the Economy
|
U.S. Global Investors Disclaimer
All opinions expressed and data provided are subject to change without notice. Some of these opinions may not be appropriate to every investor. By clicking the link(s) above, you will be directed to a third-party website(s). U.S. Global Investors does not endorse all information supplied by this/these website(s) and is not responsible for its/their content.
MVIS Global Rare Earth/Strategic Metals Index covers the largest and most liquid companies which are active in the rare earth/strategic metals sector. The index is reviewed on a quarterly basis, float market capitalization weighted, and the maximum component weight is 8%. The MSCI World Metals & Mining Index is a free float weighted equity index. Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is the rate of return that would be required for an investment to grow from its beginning balance to its ending balance, assuming the profits were reinvested at the end of each year of the investment’s life span.
Holdings may change daily. Holdings are reported as of the most recent quarter-end. The following securities mentioned in the article were held by one or more accounts managed by U.S. Global Investors as of (06/30/2021): Standard Lithium Ltd., Polymetal International PLC
Stay up to date. Follow us:

|