
The Business of Football, How the NFL Makes Money
There’s a lot of money being made through the business of professional sports leagues. The NBA, MLB, NHL, all have very profitable business models, and although the businesses are all similar, the NFL leads the other U.S. based leagues in generating revenue. The once tax-exempt entity has a dual business structure with multiple layers of income that continues to expand. Below we cover the multiple ways the NFL, and the months-long drive of more than 30 teams to the Superbowl, ring the register.
In 2015, the National Football League forfeited its tax-exempt status with the IRS. The league had benefitted from the unique status beginning in 1942. The decision was based in part on mounting criticism over its rapidly growing earnings streams.
These streams largely come from the 32 teams that make up the NFL, thirty-one of the ball clubs are privately owned, while just one, the Green Bay Packers, continues to operate under a non-profit public corporation status. The clubs all form a trade association through which funds are directed back to the NFL board, some find their way distributed back to the teams.
This form of entertainment rakes in money on many fronts. In-person attendance, TV viewers, different forms of wagering, and advertising dollars all feed into overall league revenue after costs such as salaries that can $50 million annually.
Tickets to the Super Bowl 2023 event between the Kansas City Chiefs and the Philadelphia Eagles are averaging about $10,000. The higher end seats are in the $40,000 range, about the same as a Tesla Model S.
Tax Exemption of Teams
The team with tax-exempt status is exempt from paying all or some of federal income taxes. This status had been maintained by all NFL teams from 1945 through 2015.
The NFL voluntarily opted to give up its tax-exempt status in 2015 and began paying taxes. Some contend this change avoids further negative public outcry. It seems the economic benefits were not as significant as the public relations disadvantages.
Business Structure
The league separates its income streams into local and national categories. On the national side, the NFL negotiates national merchandise, licensing, and television contracts. The 32 teams receive equal shares of this money, regardless of individual team performance.
Local income is generated through concession sales, ticket sales, and corporate sponsors. This doesn’t nearly cover the cost of fielding a professional football team. Using the Green Bay Packers as a benchmark, the team had expenses totaling $410 million in its fiscal year 2021. Most of this number was attributable to player salaries, with the remainder used for stadium maintenance, advertising, and team and administration expenses.
How Teams Make Money
The majority of any NFL team’s revenue comes from TV arrangements. Ticket revenues, licensing, merchandising agreements, and endorsement deals are additional income sources.
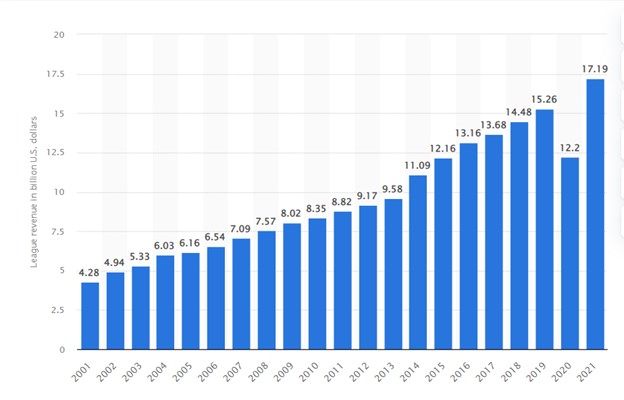
Revenue of All National Football League Teams from 2001 to 2021 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Televised Rights and Deals – The Super Bowl is among the most watched television events in America each year. The regular games broadcast on Sundays, Mondays, and Thursdays throughout the regular season will consistently have the best TV ratings. This is why media corporations pay an above average amount for the right to broadcast them.
The traditional television industry now competes with other video-based programming, all pulling the attention of those seeking entertainment. The NFL audience and draw are not in decline. NFL teams still generate massive local and even international revenue through TV contracts. The individual clubs receive significant amounts from television providers thanks to multibillion-dollar contracts, and there are even more television viewers and broadcasts of games than other programs on set.

Tickets and Vendor Rental – Far below the rapidly increasing money from TV deals, ticket sales are a large source of income for individual teams. NFL games often sell out, with an estimated average ticket price of $151 and a stadium capacity of roughly 70,000. It’s a nice add-on to broadcast viewership.
NFL teams can also use their stadiums to hold non-football activities, like concerts within local restrictions.
The cash flow on the rental of space to vendors to sell food and drinks at games are also significant in a stadium with 70,000 fans as a captive audience.

Official Sponsorships – Corporate sponsors pay NFL teams to put their logos on products, TV transitions, player jerseys, etc. The franchise rights to NFL grounds naming of stadiums are extremely desirable among corporate advertisers.
The naming right to So-Fi Stadium in LA, home of the Los Angeles Rams, is in the neighborhood of $30 million annually, and similar rights to Allegiant Stadium in Las Vegas is estimated at between $20 and $25 million annually.
Gambling Franchises – Some NFL teams take advantage of this method by opening betting platforms in their stadiums, collaborating with well-known casinos, creating online sports betting websites, and other strategies. This is an area of rapid expansion as sports betting becomes legalized across the US and technology provides opportunities for betting on fragments of the game in addition to the more traditional methods. Incremental income from these growing arrangements has expanded income opportunities among teams.

Costs
Overall, like any business, the NFL will undoubtedly explore all the opportunities for meaningful income that present itself. Of course the overall income is best measured net of expenditures that include marketing, cost of athletes and other entertainers, management, upkeep, and renovations.
Take Away
One of the most financially successful professional sports leagues in the US and across the globe is the NFL. Most of the teams’ revenues are generated from broadcasting and licensing deals. The growth in revenue, with the exception of one year during the pandemic curbs, has been accelerating. Technology has brought new methods to gamble on sports, along with some friendly gaming legislation across the nation. This is additive to the bottom line.
It appears that the trend, which has survived some public relations setbacks, isn’t going to continue as Americans tend to spend many hours during the winter months immersed in the sport of football.
Managing Editor, Channelchek