
Fragile Investor Confidence Could Create Greater Repercussions, Says Moody’s
Bankdemic?
Moody’s Investors Service is cautiously optimistic bank problems will not spill over into the broader economy. However, in a new report, this top-three rating agency said they believe the financial regulators have acted in a way to prevent ripple effects from stressed banks, but they admit there is a good deal of uncertainty in both investor confidence and the economy as a whole. Moody’s wrote that “there is a risk that policymakers will be unable to curtail the current turmoil without longer-lasting and potentially severe repercussions within and beyond the banking sector.”
The reason for the rating services concern is, “even before bank stress became evident, we had expected global credit conditions to continue to weaken in 2023 as a result of significantly higher interest rates and lower growth, including recessions in some countries.” Moody’s said that the longer financial conditions remain tight, the greater the chance that industries outside of banking will experience problems.
Moody’s outlined three channels by which bank problems could become contagious to other sectors.
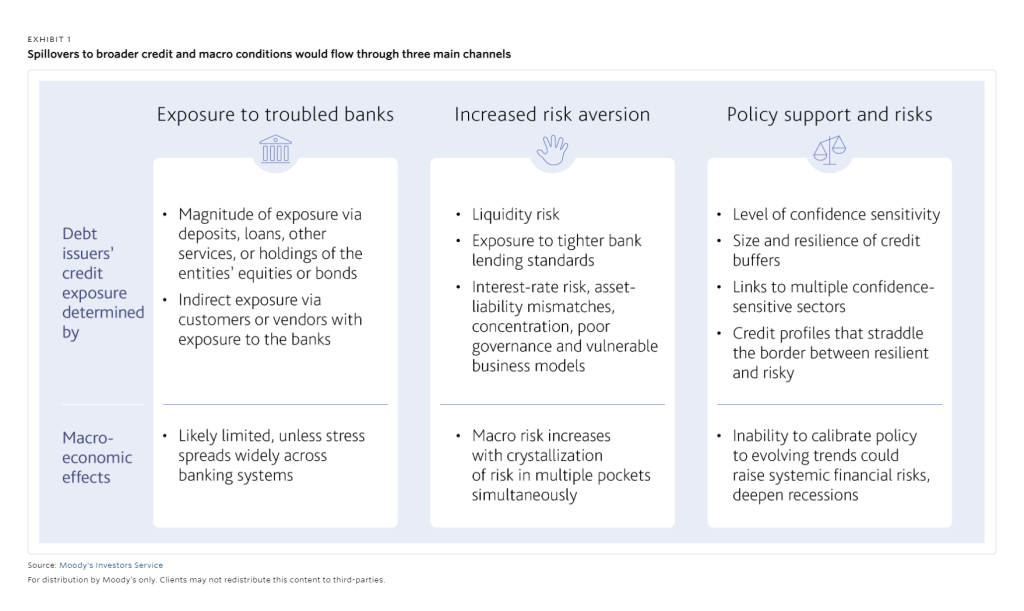
Three Spillover Channels Risks Defined
The first and most possible channel would be the problems encountered by entities with direct and indirect exposure to troubled banks. These can come in different forms. Financial and nonfinancial entities in the private and public sectors could have direct exposure to banks via deposits, loans, other transactional facilities, or direct holdings of weakened banks’ stocks or bonds. Unrelated, they may rely on a troubled bank for services essential to their business.
As it relates to this first channel, the rating agency wrote, “Monitoring and evaluating the direct and indirect links at the entity level will be a key focus of our credit analysis over the coming weeks and months.” Moody’s mentioned Credit Suisse by name in their note, saying the consequences of the UBS takeover are still unfolding, “Given the size and systemic importance of Credit Suisse, there likely will be varied consequences of its takeover for a range of financial actors with direct exposure to the bank.” The rating agency also believes the rapid completion of the deal appears to have avoided widespread contagion across the banking sector.”
The second channel Moody’s indicates could be most potent. It is that broader problems within the banking sector would cause banks to have stricter lending practices. Moody’s says that if this occurred, it would impact customers that are “liquidity-constrained.” The domino impact would then be that investors and lenders may become more cautious, “with particular regard to entities that are exposed to risks similar to those of the troubled banks.”
From this scenario, there is a potential for shocks from interest rate risk, asset-liability mismatches, a large imbalance of assets or liabilities, poor governance, weak profits, and higher leverage.
The third risk is seen as policy risk. For policymakers whose main focus is taming inflation, the bank problems pose additional challenges to steering the economy to a soft landing. Policy actions and expectations will continue to serve to shape market sentiment. Moody’s baseline case forecasts that it expects policy responses to be rapid if risks emerge. This could help keep entity-level issues from becoming systemic problems. Moody’s note recognizes that policy and implementation are challenging, and there are risks of policy missteps, limitations, or unintended consequences.
“One key policy challenge is how policymakers will address both inflation and financial stability risks,” Moody’s explained that inflation is still high and labor market strength continues. “the failure to rein in inflation now could lead to de-anchoring of inflation expectations and increased nominal bond yields, forcing even more tightening later to restore monetary policy credibility.”
Moody’s wrote that the actions taken by the central banks, and financial regulators show that they recognize the importance of agility and coordination to address arising problems while not acting in a way to add more stress and create a systemic crisis.
Take Away
The recent downfall of a few banks demonstrates how pulling liquidity out of an overly stimulated economy can cause withdrawal pains. Whether the new, tighter credit conditions will tip the economy into a deeper economic downturn as the spillover effect spreads to other sectors remains to be seen. If it occurs, Moody’s expects it would come from the interplay between preexisting credit risks, policy actions, and market sentiment. But, its role as a rating agency is to highlight possible risks. This is not a forecast, there forecast is that regulators and policymakers will have eventually succeeded to contain any ripple effects.
Managing Editor, Channelchek
Source